Effect of Iron Rich Foods SMS Intervention on Iron Intake in Pregnant Women with Anemia
Abstract
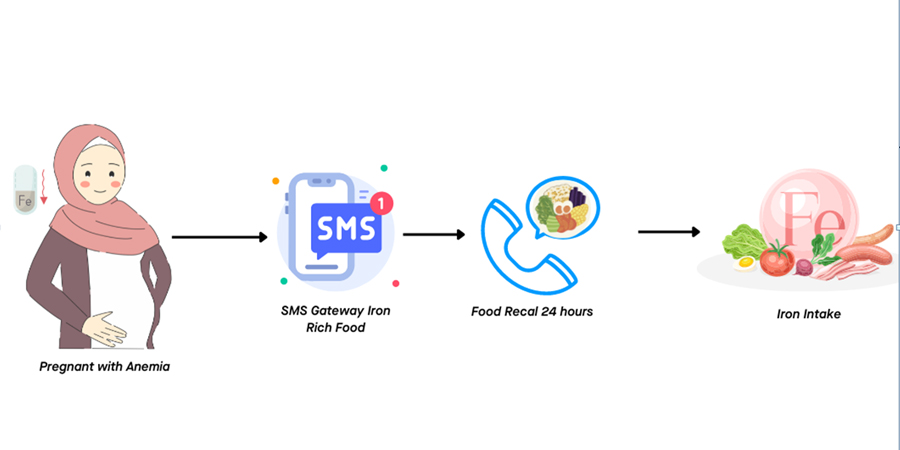
Pregnancy-related anemia has been linked to many undesirable consequences for both mothers and their children. Prevention of anemia in pregnant women can be supported through health promotion media such as SMS-gateway. This study was focused on knowing the effect of SMS gateway knowledge about foods high in iron on intake of foods high in iron in anemic pregnant women. The study was used a double-blind randomized controlled trial to analyze the effect of SMS intervention on iron-rich food on 68 anemic pregnant women at seven health centers in Makassar City. The intervention applied the software Gili SMS® to deliver SMS interventions. The intervention was given on days 3, 10, 17, and 24 of the study, and food recalls were carried out on days 0 and 28 of the study using the 24-hour food recall method. We found that there was no significant difference on intake of iron but a significant difference between intake of energy and carbohydrate between control and intervention group after SMS gateway intervention. By the recommendations in one of the verses in the Qur'an, pregnant women are encouraged to choose and consume good food such as vegetable and animal protein produced by plants and animals. Foods are suitable for the body and provide all the nutrients needed for the body's normal functioning. We found no increased of iron intake after SMS intervention in pregnant women with anemia.
Downloads
References
Abd Rahman, R., Idris, I. B., Md Isa, Z., & Abd Rahman, R. (2022). The effectiveness of a theory-based intervention program for pregnant women with anemia: A randomized control trial. Plos one, 17(12), e0278192. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0278192
Adjei-Banuah, N. Y., Aduah, V. A., Ziblim, S. D., Ayanore, M. A., Amalba, A., & Mogre, V. (2021). Nutrition Knowledge is Associated With the Consumption of Iron Rich Foods: A Survey Among Pregnant Women From a Rural District in Northern Ghana. Nutrition and Metabolic Insights, 14. https://doi.org/10.1177/11786388211039427
Badan Pusat statistik. (2016). Profil Penduduk Indonesia Hasil Survei Penduduk Antar Sensus (SUPAS) 2015. https://lmsspada.kemdikbud.go.id/mod/resource/view.php?id=87857
Bhattarai, S., Yadav, S. K., Thapaliya, B., Giri, S., Bhattarai, B., Sapkota, S., Hillman, S., Baral, S. C., & Morrison, J. (2023). Contextual factors affecting the implementation of an anemia focused virtual counseling intervention for pregnant women in plains Nepal: a mixed methods process evaluation. BMC public health, 23(1), 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-023-16195-5
Chaparro, C. M., & Suchdev, P. S. (2019). Anemia epidemiology, pathophysiology, and etiology in low- and middle-income countries. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1450(1), 15–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.14092
Handari, S. R. T., Anies, Kartasurya, M. I., & Nugraheni, S. A. (2022). Haemoglobin Level of Pregnant Women was Associated with History of Anemia During Adolescent Period: Findings from the Indonesia Family Life Survey. Bali Medical Journal, 11(3), 1710–1716. https://doi.org/10.15562/bmj.v11i3.3783
Herlina, S. (2018). Evaluasi Hasil Penerapan Model Sms Gateway Dalam Promosi Kesehatan Tentang Bahaya Komplikasi Selama Kehamilan. Seminar Nasional Informatika Medis (SNIMed), 68–76. https://journal.uii.ac.id/snimed/article/view/11886
Hidayatunnikmah, N. (2021). Level of education, knowledge of pregnant women regarding iron tablets to compliance with their consumption. Jurnal Kesehatan LLDikti Wilayah 1 (JUKES), 1(1), 15–21. https://doi.org/10.54076/jukes.v1i1.126
Ibikunle, H. A., Okafor, I. P., & Adejimi, A. A. (2021). Pre-natal nutrition education: Health care providers’ knowledge and quality of services in primary health care centres in Lagos, Nigeria. PLoS ONE, 16(11 November), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0259237
Kementerian Kesehatan RI. (2016). Pedoman Pencegahan dan Penanggulangan Anemia Pada Remaja Putri dan Wanita Usia Subur (WUS). In Direktorat Gizi Masyarakat Kemenkes RI. https://ayosehat.kemkes.go.id/buku-pedoman-pencegahan-dan-penanggulangan-anemia-pada-remaja-putri-dan-wanita-usia-subur
Pembangunan Nasional. (2020). Pilar Pembangunan Sosial. https://sdgs.bappenas.go.id/website/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/Metadata-Pilar-Sosial-Edisi-II.pdf
Khotimah, H., Ginting, M., & Jaladri, I. (2019). Pengaruh Edukasi Gizi Melalui Media Facebook Terhadap Pengetahuan Anemia Dan Konsumsi Protein, Zat Besi, Dan Vitamin C Pada Remaja Putri. 2(1), 1–3. https://ejournal.polkespon.ac.id/index.php/PNJ/article/view/477
Malhotra, U., Roy, M., Sontakke, M., & Choudhary, P. (2023). A recent paradigm on iron absorption, prevalence, and emerging dietary approaches to eradicate iron deficiency. Food Bioengineering, February, 53–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/fbe2.12042
Marfuah, D., & Kusudaryati, D. P. D. (2020). Pengaruh Edukasi Gizi terhadap Pengetahuan Gizi dan Asupan Zat Besi pada Remaja Putri. PROFESI (Profesional Islam): Media Publikasi Penelitian, 18(2), 116–123. https://journals.itspku.ac.id/index.php/profesi/article/download/73/26
Mousa, A., Naqash, A., & Lim, S. (2019). Macronutrient and micronutrient intake during pregnancy: An overview of recent evidence. Nutrients, 11(2), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020443
Nadiyah, Meilinda br Sembiring Meliala, E., Cristina Simanjuntak, A., & Misalsalina Perangin-Angin, F. (2021). Relationship between Characteristics and Nutrient Intake with Anemia among Pregnant Women at Kebon Jeruk Public Health Center, Jakarta. International Journal of Nursing and Health Services (IJNHS), 3(2), 303–312. https://doi.org/10.35654/ijnhs.v4i3.454
Nahrisah, P., Somrongthong, R., Viriyautsahakul, N., Viwattanakulvanid, P., & Plianbangchang, S. (2020). Effect of integrated pictorial handbook education and counseling on improving anemia status, knowledge, food intake, and iron tablet compliance among anemic pregnant women in Indonesia: A quasi-experimental study. Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare, 13, 43–52. https://doi.org/10.2147/JMDH.S213550
Peiris, D. R., Wijesinghe, M. S. D., Gunawardana, B. M. I., Weerasinghe, W. M. P. C., Rajapaksha, R. M. N. U., Rathnayake, K. M., Ranathunga, N., Kalupahana, S., Supun, Y. A., Deshpande, S., & Ahmed, F. (2023). Mobile Phone-Based Nutrition Education Targeting Pregnant and Nursing Mothers in Sri Lanka. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032324
Permenkes Republik Indonesia Nomor 28 Tahun 2019. (2019). Angka Kecukupan Gizi Yang Dianjurkan Untuk Masyarakat Indonesia. https://peraturan.bpk.go.id/Home/Details/138621/permenkes-no-28-tahun-2019
Safiri, S., Kolahi, A. A., Noori, M., Nejadghaderi, S. A., Karamzad, N., Bragazzi, N. L., Sullman, M. J. M., Abdollahi, M., Collins, G. S., Kaufman, J. S., & Grieger, J. A. (2021). Burden of anemia and its underlying causes in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Journal of Hematology and Oncology, 14(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-021-01202-2
Sahoo, K. C., Negi, S., Patel, K., Mishra, B. K., & Palo, S. K. (2021). Challenges in Maternal and Child Health Services Delivery and Access during Pandemics or Public Health Disasters in. Healthcare Review MDPI, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9070828
Skolmowska, D., Głąbska, D., Kołota, A., & Guzek, D. (2022). Effectiveness of dietary interventions in prevention and treatment of iron-deficiency anemia in pregnant women: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Nutrients, 14(15), 3023. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153023
Sugiharti, R. K., & Cahyaningrum, E. D. (2020). The Correlation Between Family Income and Mom’s Education with Anemia. ICCH 2019, 20, 94–96. https://doi.org/10.2991/ahsr.k.200204.022
Sunuwar, D. R., Sangroula, R. K., Shakya, N. S., Yadav, R., Chaudhary, N. K., & Pradhan, P. M. S. (2019). Effect of nutrition education on hemoglobin level in pregnant women: A quasi-experimental study. PLoS ONE, 14(3), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0213982
Tarigan, N., Sitompul, L., & Zahra, S. (2021). Asupan Energi, Protein, Zat Besi, Asam Folat Dan Status Anemia Ibu Hamil Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Petumbukan. Wahana Inovasi: Jurnal Penelitian Dan Pengabdian Masyarakat, 10(1), 118–127. https://jurnal.uisu.ac.id/index.php/wahana/article/view/4325/3103
Teweldemedhin, L. G., Amanuel, H. G., Berhe, S. A., Gebreyohans, G., Tsige, Z., & Habte, E. (2021). Effect of nutrition education by health professionals on pregnancy-specific nutrition knowledge and healthy dietary practice among pregnant women in Asmara, Eritrea: A quasi-experimental study. BMJ Nutrition, Prevention and Health, 4(1), 181–194. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000159
Wardono, Y. S. (2020, Januari 29). Gili SMS. http://www.yusiwa.com/
World Health Organization. (2019). Maternal mortality: evidence brief. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/329886
Zhang, J., Li, Q., Song, Y., Fang, L., Huang, L., & Sun, Y. (2022). Nutritional factors for anemia in pregnancy: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Frontiers in Public Health, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.1041136
Copyright (c) 2023 Nadhirah Ananda Idris, Andi Faradilah, Rauly Ramadhani, Henny Fauziah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted to publish their work online in third parties as it can lead to wider dissemination of the work.




