Nutrition and Breastfeeding in the View of Islam to Prevent Acute Respiratory Infections in Toddlers
Abstract
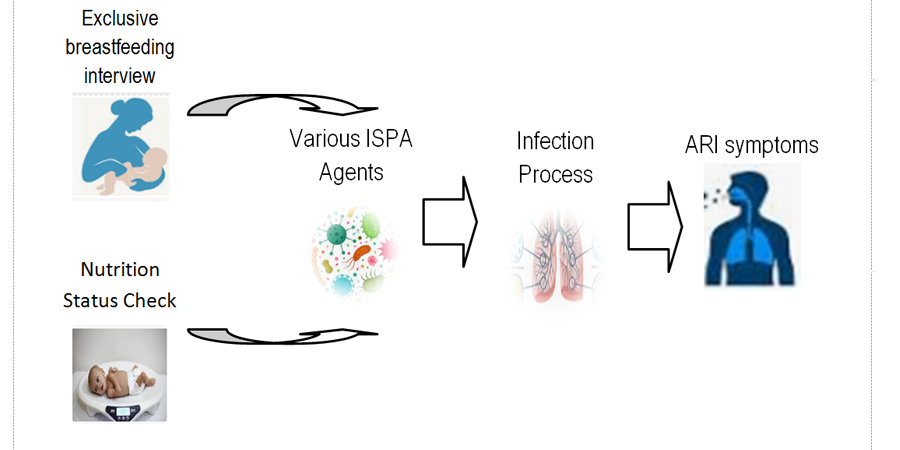
Acute Respiratory Infection (ARI) in Indonesia generally occurs in urban areas and always ranks first as a cause of death in infants or toddlers. Studies on the incidence of ISPA in toddlers in rural areas are still rarely studied. This study aims to analyze the relationship between nutritional status and exclusive breastfeeding with the incidence of ARI in toddlers. This study was an analytic survey study with a case-control design. The population in this study consisted of 68 toddlers diagnosed with ISPA and all of them were sampled with a ratio of 1:1 and the total sample was 136 people. The toddler's mother pleaded as the respondent. The instruments used were questionnaires and health cards (KMS) for toddlers. Data analysis used is chi square. Statistical analysis of the relationship between nutritional status and the incidence of ARI (P=0.001) and the relationship between exclusive breastfeeding and ARI was obtained (P=0.001). This means that there is a significant relationship between nutritional status and exclusive breastfeeding program and the incidence of ARI. Nutritional status and exclusive breastfeeding programs contribute to the incidence of ARI among toddlers in rural areas. This study recommends that mothers prioritize giving primary food to babies in the form of exclusive breastfeeding for 2 years according to the guidance of the Koran. This action will greatly affect the nutritional status of toddlers, especially in preventing ARI.
Downloads
References
Ahmed, K. Y., Page, A., Arora, A., Ogbo, F. A., & Global Maternal and Child Health Research collaboration (GloMACH). (2020). Associations between infant and young child feeding practices and acute respiratory infection and diarrhoea in Ethiopia: A propensity score matching approach. PloS one, 15(4), e0230978. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0230978
Andreas, N. J., Kampmann, B., & Le-Doare, K. M. (2015). Human breast milk: A review on its composition and bioactivity. Early human development, 91(11), 629-635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2015.08.013
Ardila, A., Noraida, N., & Erminawati, E. (2019). Perilaku merokok orangtua dengan kejadian ISPA pneumonia pada balita. Jurnal Kesehatan Lingkungan: Jurnal dan Aplikasi Teknik Kesehatan Lingkungan, 16(1), 707-714. https://doi.org/10.31964/jkl.v16i1.138
Ariano, A., Bashirah, A. R., Lorenza, D., Nabillah, M., Apriliana, S. N., & Ernawati, K. (2019). Hubungan Faktor Lingkungan dan Perilaku Terhadap Kejadian Infeksi Saluran Pernafasan Akut (ISPA) di Desa Talok Kecamatan Kresek. Jurnal Kedokteran Yarsi, 27(2), 076-083. https://doi.org/10.33476/jky.v27i2.1119
Balogun, O. O., Dagvadorj, A., Anigo, K. M., Ota, E., & Sasaki, S. (2015). Factors influencing breastfeeding exclusivity during the first 6 months of life in developing countries: a quantitative and qualitative systematic review. Maternal & child nutrition, 11(4), 433-451. https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.12180
Calder, P. C., Carr, A. C., Gombart, A. F., & Eggersdorfer, M. (2020). Optimal nutritional status for a well-functioning immune system is an important factor to protect against viral infections. Nutrients, 12(4), 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041181
Chandra, C. (2017). Hubungan pendidikan dan pekerjaan ibu dengan upaya pencegahan ISPA pada balita oleh ibu yang berkunjung ke Puskesmas Kelayan Timur Kota Banjarmasin. An-Nadaa: Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat (e-Journal), 4(1), 11-15. http://dx.doi.org/10.31602/ann.v4i1.976
Dinas Kesehatan Provinsi Sulawesi Tenggara. 2022. Profil Kesehatan Sulawesi Tenggara Tahun 2020. https://dinkes.sultengprov.go.id/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/profil-kesehatan-tahun-2020.pdf.
Fadlila, F., & Rahmawaty, I. (2015). Hubungan antara Pemberian ASI Eksklusif dan Non Eksklusif dengan Kejadian Pneumonia pada Balita. Prosiding Pendidikan Dokter, 774-779. http://dx.doi.org/10.29313/kedokteran.v0i0.1459
Freeman, M. C., Garn, J. V., Sclar, G. D., Boisson, S., Medlicott, K., Alexander, K. T., Rehfuess E. A., & Clasen, T. F. (2017). The impact of sanitation on infectious disease and nutritional status: A systematic review and meta-analysis. International journal of hygiene and environmental health, 220(6), 928-949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2017.05.007
Ghimire, P., Gachhadar, R., Piya, N., Shrestha, K., & Shrestha, K. (2022). Prevalence and factors associated with acute respiratory infection among under-five children in selected tertiary hospitals of Kathmandu Valley. Plos one, 17(4), e0265933. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0265933
Giroth, T. M., Manoppo, J. I. C., & Bidjuni, H. J. (2022). Hubungan Status Gizi Dengan Kejadian Ispa Pada Balita Di Puskesmas Tompaso Kabupaten Minahasa. Jurnal Keperawatan, 10(1), 79-85. https://doi.org/10.35790/jkp.v10i1.36338
Hassen, S., Getachew, M., Eneyew, B., Keleb, A., Ademas, A., Berihun, G., Kebede, A. B., & Sisay, T. (2020). Determinants of acute respiratory infection (ARI) among under-five children in rural areas of Legambo District, South Wollo Zone, Ethiopia: A matched case–control study. International Journal of Infectious Diseases, 96, 688-695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.012
Hernández-Díaz, I., Ayala-Meléndez, A., González-González, E., Rosario-Calderón, I., Figueroa-Ríos, D., Melin, K., & Hernández-Muñoz, J. J. (2019). Knowledge and beliefs, behaviors, and adherence among Latino parents or legal guardians related to antibiotic use for upper respiratory tract infections in children under 6 years of age. Journal of the American Pharmacists Association, 59(4), 506-513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.japh.2019.03.004
Irma, I., & Masluhiya, S. (2020). Perbedaan karakteristik keluarga dengan kejadian gizi kurang pada balita Suku Bajo dan Non bajo di wilayah pesisir Kota Kendari. Care: Jurnal Ilmiah Ilmu Kesehatan, 8(1), 74-83. https://doi.org/10.33366/jc.v8i1.1668
Irma, I., Sabilu, Y., Muchtar, F., & Zainuddin, A. (2021). Pengaruh Infeksi Penyakit Tropis terhadap Kejadian Gizi Kurang pada Balita di Wilayah Kabupaten Buton Utara. Jurnal Ilmiah Kesehatan, 20(2), 83-88. https://doi.org/10.33221/jikes.v20i2.652
Ismail, H. (2018). Syariat menyusui dalam alquran (kajian Surat Al-Baqarah ayat 233). Jurnal At-Tibyan: Jurnal Ilmu Alqur'an dan Tafsir, 3(1), 56-68. https://doi.org/10.32505/at-tibyan.v3i1.478
Kemenkes RI. 2014. Peningkatan Kesehatan Ibu Dan Anak Bagi Bidan Dan Perawat. Pusat Promosi Kesehatan Kementerian Kesehatan. https://promkes.kemkes.go.id/pub/files/files45265Layout_Peningkatan_Kesehatan_Ibu_dan_Anak_untuk_Bidan_dan_Perawat.pdf.
Mulatya, D. M., & Mutuku, F. W. (2020). Assessing comorbidity of diarrhea and acute respiratory infections in children under 5 years: evidence from Kenya’s demographic health survey 2014. Journal of primary care & community health, 11, 2150132720925190. https://doi.org/10.1177/2150132720925190
Nhung, N. T. T., Schindler, C., Dien, T. M., Probst-Hensch, N., Perez, L., & Künzli, N. (2018). Acute effects of ambient air pollution on lower respiratory infections in Hanoi children: an eight-year time series study. Environment international, 110, 139-148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.10.024
Nurfitriani, N. (2022). Konsep Al-Qur’an dan Hadis Tentang Radha’ah dan Hadhanah Perspektif Gender. SANGAJI: Jurnal Pemikiran Syariah dan Hukum, 6(1), 51-70. https://doi.org/10.52266/sangaji.v6i1.772
Pinzón-Rondón, Á. M., Aguilera-Otalvaro, P., Zárate-Ardila, C., & Hoyos-Martínez, A. (2016). Acute respiratory infection in children from developing nations: a multi-level study. Paediatrics and international child health, 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1080/20469047.2015.1109252
Robi'aqalbi, R. (2019). Kebenaran dan Peranan Al-Qur’an dalam Kesempurnaan Sistem Imun Tubuh Manusia. Al-I’jaz: Jurnal Studi Al-Qur’an, Falsafah Dan Keislaman, 1(2), 40-55. https://doi.org/10.53563/ai.v1i2.22
Sari, L. M. (2019). Hubungan ASI Eksklusif dengan Kejadian ISPA Pada Balita (0-59 Bulan) Di Puskesmas Pembina Palembang Tahun 2017. Jurnal Kesehatan dan Pembangunan, 9(18), 43-48. https://doi.org/10.52047/jkp.v9i18.42
Septiawati, D., Indriani, Y., & Zuraida, R. (2021). Tingkat Konsumsi Energi dan Protein dengan Status Gizi Balita. Jurnal Ilmiah Kesehatan Sandi Husada, 10(2), 598-604. https://doi.org/10.35816/jiskh.v10i2.660
Sirait, S. H. (2017). Pengaruh pemberian Asi eksklusif dengan kejadian ISPA pada anak Batita di Puskesmas Singosari Kota Pematangsiantar. Global Health Science, 2(1), 70-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.33846/ghs.v2i1.74
Sunarni, N., Litasari, R., & Deis, L. (2017). Hubungan status gizi dengan kejadian ISPA pada balita di wilayah kerja puskesmas Margaharja Sukadana Ciamis. Jurnal Riset Kebidanan Indonesia, 1(2), 70-75. https://doi.org/10.32536/jrki.v1i2.11
UNICEF. 2020. “Every Child ’s Right To Survive : An Agenda To End Pneumonia Deaths. 1–12. https://data.unicef.org/org/topic/childhealt/pneumonia.
Wang, Y., Li, Y., Liu, J., Zhao, Y., Xie, Z., Shen, J., & Tan, W. (2016). Genetic characterization of human bocavirus among children with severe acute respiratory infection in China. Journal of Infection, 73(2), 155-163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2016.05.014
Windi, R., Efendi, F., Qona'ah, A., Adnani, Q. E. S., Ramadhan, K., & Almutairi, W. M. (2021). Determinants of acute respiratory infection among children under-five years in Indonesia. Journal of Pediatric Nursing, 60, e54-e59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedn.2021.03.010
Copyright (c) 2023 Irma Irma, Kamrin Kamrin, Kamrin Kamrin, Harleli Harleli

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted to publish their work online in third parties as it can lead to wider dissemination of the work.




