Behind the Hammer's Swing: Work Fatigue Among Traditional Stone Breakers in the Coastal Region of the Selayar Islands, Indonesia
Abstract
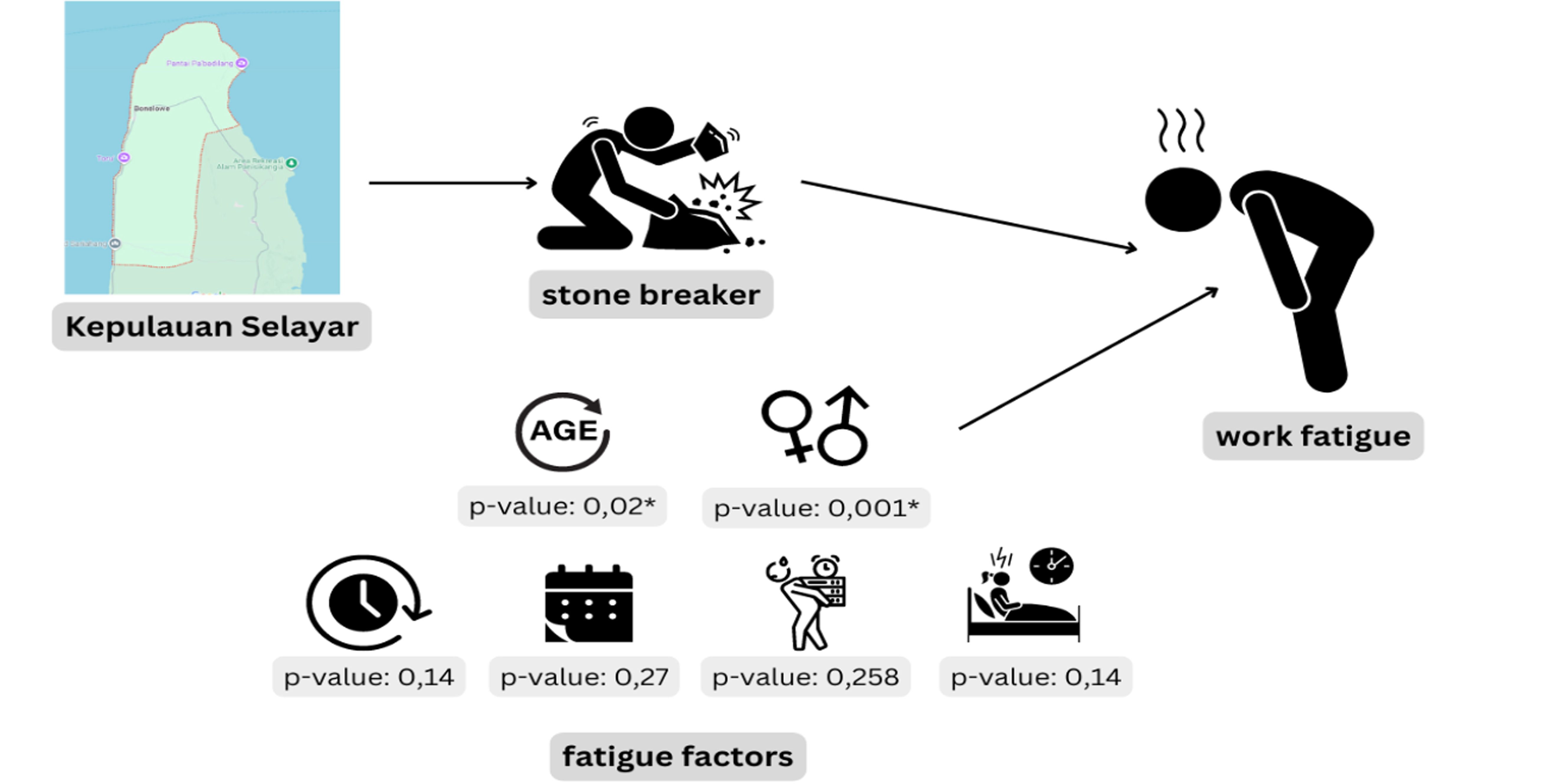
The work of stone breakers involves heavy and repetitive physical activity, which can increase the risk of injuries and health problems, one of which is work fatigue. Before work fatigue becomes more severe, it is essential to identify its causes. This study aims to analyze work fatigue and the factors that influence it. The study uses an observational analytic approach with a total of 50 respondents. The variables measured include age, length of work, years of service, workload, total sleep time, and work fatigue. Data collection was carried out through questionnaires and specific workload observations. The results of the study indicate that 25 people (50%) experienced high work fatigue. Further analysis showed that age (p-value = 0.020) and gender (p-value = 0.001) significantly influenced work fatigue. The results also showed that there was no significant effect of length of work (p-value = 0.140), years of service (p-value = 0.27), workload (p-value = 0.258), and total sleep time (p-value = 0.401) on work fatigue. This study concludes that work fatigue among traditional stone breakers is influenced by age and gender. Interventions are needed to reduce work fatigue through adjustments to the work environment and rest periods. This study reinforces the understanding of Q.S. Al-Baqarah/2:286, which emphasizes that every individual has limitations. The fatigue experienced is proof that the human body has limits and needs adequate rest to function optimally.
Downloads
References
Aagaard, P., Suetta, C., Caserotti, P., Magnusson, S. P., & Kjær, M. (2010). Role of the nervous system in sarcopenia and muscle atrophy with aging: Strength training as a countermeasure. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine and Science in Sports, 20(1), 49–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0838.2009.01084.x
Agostini, A., Lushington, K., & Dorrian, J. (2019). The relationships between bullying, sleep, and health in a large adolescent sample. Sleep and Biological Rhythms, 17, 172–182. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1007/s41105-018-0197-z
Allison, P., Tiesman, H. M., Wong, I. S., Bernzweig, D., James, L., James, S. M., & Patterson, P. D. (2022). Working hours, sleep, and fatigue in the public safety sector: A scoping review of the research. American journal of industrial medicine, 65(11), 878-897. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajim.23407
Amalianah, R., Sutangi, & Rahmawati, Ad. (2022). Faktor-Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi Terhadap Kelelahan Kerja Pada Pekerja Pengisian Air Minum Dalam Kemasan Di PT Bharata Sakti Persada Indramayu Tahun 2021. Afiasi : Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat, 7(2), 288–292. https://doi.org/10.31943/afiasi.v7i2.220
Antika, R., & Prameswari, G. N. (2023). Hubungan Masa Kerja, Usia, Status Gizi, Kecukupan Energi, Kebiasaan Merokok dengan Kelelahan Kerja pada PEtani Padi. Indonesia Journal of Public Health and Nutrition, 3(1), 127–136. https://doi.org/10.15294/ijphn.v3i1.53917
Antoni, F., & Widanarko, B. (2023). Durasi Kerja Harian sebagai Determinan Utama Kelelahan Pekerja House Keeping. Jurnal Penelitian Kesehatan Suara Forikes, 14(3). http://dx.doi.org/10.33846/sf14303
Anwer, S., Li, H., Antwi-Afari, M. F., Umer, W., & Wong, A. Y. L. (2021). Evaluation of physiological metrics as real-time measurement of physical fatigue in construction workers: state-of-the-art review. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 147(5), 03121001. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0002038
Argyle, E. M., Marinescu, A., Wilson, M. L., Lawson, G., & Sharples, S. (2021). Physiological indicators of task demand, fatigue, and cognition in future digital manufacturing environments. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 145, 102522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhcs.2020.102522
Ávila-Gutiérrez, M. J., Suarez-Fernandez de Miranda, S., & Aguayo-González, F. (2022). Occupational safety and health 5.0—A model for multilevel strategic deployment aligned with the sustainable development goals of agenda 2030. Sustainability, 14(11), 6741. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116741
Baraniuk, J. N. (2022). Review of the midbrain ascending arousal network nuclei and implications for myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), Gulf War Illness (GWI) and Postexertional Malaise (PEM). Brain Sciences, 12(2), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12020132
Behm, D. G., Alizadeh, S., Hadjizedah Anvar, S., Hanlon, C., Ramsay, E., Mahmoud, M. M. I., & Steele, J. (2021). Non-local muscle fatigue effects on muscle strength, power, and endurance in healthy individuals: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Sports Medicine, 51, 1893-1907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-021-01456-3
Behrens, M., Gube, M., Chaabene, H., Prieske, O., Zenon, A., Broscheid, K. C., & Weippert, M. (2023). Fatigue and human performance: an updated framework. Sports medicine, 53(1), 7-31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-022-01748-2
Bendak, S., & Rashid, H. S. (2020). Fatigue in aviation: A systematic review of the literature. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 76, 102928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ergon.2020.102928
Bláfoss, R., Sundstrup, E., Jakobsen, M. D., Brandt, M., Bay, H., & Andersen, L. L. (2019). Physical workload and bodily fatigue after work: Cross-sectional study among 5000 workers. European Journal of Public Health, 29(5), 837–842. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurpub/ckz055
Cheng, Q. S., Liu, T., Huang, H. B., Peng, Y. F., Jiang, S. C., & Mei, X. B. (2017). Association between personal basic information, sleep quality, mental disorders and erectile function: a cross-sectional study among 334 Chinese outpatients. Andrologia, 49(3). https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/and.12631
Cunningham, C., O'Sullivan, R., Caserotti, P., & Tully, M. A. (2020). Consequences of physical inactivity in older adults: A systematic review of reviews and meta‐analyses. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports, 30(5), 816-827. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.13616
Darchia, N., Oniani, N., Sakhelashvili, I., Supatashvili, M., Basishvili, T., Eliozishvili, M., Maisuradze, L., & Cervena, K. (2018). Relationship between sleep disorders and health related quality of life—results from the georgia SOMNUS study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(8), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081588
Guduru, R. K. R., Domeika, A., & Domeikienė, A. (2022). Effect of rounded and hunched shoulder postures on myotonometric measurements of upper body muscles in sedentary workers. Applied Sciences, 12(7), 3333. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073333
Guglielmi, O., Magnavita, N., & Garbarino, S. (2018). Sleep quality, obstructive sleep apnea, and psychological distress in truck drivers: a cross-sectional study. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 53(5), 531–536. https://doi.org/0.1007/s00127-017-1474-x
Harknett, K., Schneider, D., & Wolfe, R. (2020). Losing sleep over work scheduling? The relationship between work schedules and sleep quality for service sector workers. SSM-Population Health, 12, 100681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssmph.2020.100681
Ibáñez, S. J., Perez-Goye, E., García-Rubio, J., & Courel-Ibáñez, J. (2020). Effects of task constraints on training workload in elite women’s soccer. International Journal of Sports Science & Coaching, 15(1), 99-107. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747954119891158
International Labour Organization. (2016). Workplace Stress: a collective challenge. In Workplace Stress: A collective challenge World (Issue April 2016). International Labour Organization. https://www.ilo.org/global/topics/safety-and-health-at-work/resources-library/publications/WCMS_466547/lang--en/index.htm%0Ahttp://www.ilo.org/africa/media-centre/news/WCMS_477712/lang--en/index.htm
Jean-louis, G., Turner, A. D., Seixas, A., Jin, P., Rosenthal, D. M., Liu, M., & Avirappattu, G. (2020). Epidemiologic Methods to Estimate Insu ffi cient Sleep in the US Population. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(24). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249337
Jones, M. D., Wewege, M. A., Hackett, D. A., Keogh, J. W., & Hagstrom, A. D. (2021). Sex differences in adaptations in muscle strength and size following resistance training in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Medicine, 51, 503-517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-020-01388-4
Joshi, C. K., Ranga, M. M., & Ranga, S. (2021). Silicosis: An Occupational Health Crisis Among Stone Grinders. In Multidimensional Approaches to Impacts of Changing Environment on Human Health (pp. 169-181). CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003095422-9
Juliana, M., Camelia, A., & Rahmiwati, A. (2018). Analisis Faktor Risiko Kelelahan Kerja pada Karyawan Bagian Produksi PT. Arwana aAnugrah Keramik, Tbk. Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan Masyarakat, 9(1), 53–63. https://doi.org/10.26553/jikm.2018.9.1.53-63
Kar, G., & Hedge, A. (2020). Effects of a sit-stand-walk intervention on musculoskeletal discomfort, productivity, and perceived physical and mental fatigue, for computer-based work. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 78, 102983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ergon.2020.102983
Karyati, E., Junus, S., & Hasanuddin, H. (2021). Hubungan Antara Kelelahan dan Keluhan Fisik Berdasarkan Jenis Kelamin Pada Pekerja Pengalengan Ikan. Jamura Industrial Review, 1(1), 7–14. https://doi.org/10.37905/jirev.v1i1.7772
Kenny, G. P., Yardley, J. E., Martineau, L., & Jay, O. (2008). Physical work capacity in older adults: Implications for the aging worker. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 51(8), 610–625. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajim.20600
Koohsari, M. J., Nakaya, T., McCormack, G. R., Shibata, A., Ishii, K., & Oka, K. (2021). Changes in workers’ sedentary and physical activity behaviors in response to the COVID-19 pandemic and their relationships with fatigue: longitudinal online study. JMIR public health and surveillance, 7(3), e26293. https://doi.org/10.2196/26293
Krasin, E., Schermann, H., Snir, N., Tudor, A., & Behrbalk, E. (2022). A quick and comprehensive guide to differential diagnosis of neck and back pain: a narrative review. SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine, 4(1), 232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42399-022-01321-y
Krishnan, K. S., Raju, G., & Shawkataly, O. (2021). Prevalence of work-related musculoskeletal disorders: Psychological and physical risk factors. International journal of environmental research and public health, 18(17), 9361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18179361
Leivas, E. G., Corrêa, L. A., & Nogueira, L. A. C. (2022). The relationship between low back pain and the basic lumbar posture at work: a retrospective cross-sectional study. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-021-01778-9
Lestari, A. D., Batara, A. S., & Mytthalib, N. U. (2021). Faktor yang Berhubungan dengan Kelelahan Kerja pada Karyawan di PT Sumber Graha Sejahtera Luwu. Window of Public Health, 2(6), 1145–1156. https://doi.org/10.33096/woph.v2i6.321
López-Núñez, M. I., Rubio-Valdehita, S., Diaz-Ramiro, E. M., & Aparicio-García, M. E. (2020). Psychological capital, workload, and burnout: what’s new? the impact of personal accomplishment to promote sustainable working conditions. Sustainability, 12(19), 8124. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12198124
Njaka, S., Yusoff, D. M., Anua, S. M., Kueh, Y. C., & Edeogu, C. O. (2021). Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) and their associated factors among quarry workers in Nigeria: A cross-sectional study. Heliyon, 7(2). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06130
Prakoso, D. I., Setyaningsih, Y., & Kurniawan, B. (2018). Hubungan Karakteristik Individu, Beban Kerja, dan Kualitas Tidur dengan Kelelahan Kerja apda Tenaga Kerja Kependidikan di Institusi Pendidikan X. Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat, 6(April), 88–93. https://doi.org/10.14710/jkm.v6i2.20803
Pratiwi, A. P., & Diah, T. (2023). Hubungan Faktor Internal Dengan Kelelahan Kerja Pada Tenaga Kerja Bongkar Muat. Jurnal Keolahragaan JUARA, 3(1), 31–37. https://doi.org/10.37304/juara.v3i1.9355
Rahmawati, R., & Afandi, S. (2019). Faktor yang Berhubungan dengan Kelelahan Kerja pada PErawat di RSUD Bangkinang Tahun 2019. PREPOTI: Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat, 3(2), 41–45. https://doi.org/10.31004/prepotif.v3i2.478
Rezaie, A., Godio, M., & Beyer, K. (2021). Investigating the cracking of plastered stone masonry walls under shear–compression loading. Construction and Building Materials, 306, 124831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124831
Rini, N. W. E., & Lanita, U. (2023). Analysis of The Risk Factors of Work Fatigue in Formal dan Informal Workers. JMJ Special Issues, 1(3), 257–266. https://doi.org/10.22437/jmj.v11i3.24936
Rini, W. N. E., Halim, R., & Sarah, U. (2023). Factors related to work fatigue among traffic police. Poltekita: Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan, 16(4), 429-435. https://doi.org/10.33860/jik.v16i4.1740
Rino Komalig, M., & Mamusung, N. (2020). Hubungan Antara Umur Dan Shift Kerja Dengan Kelelahan Kerja Pada Petugas Karcis Parkir Kawasan Megamas Kota Manado. Media Publikasi Promosi Kesehatan Indonesia (MPPKI), 3(1), 26–30. https://doi.org/10.56338/mppki.v3i1.1015
Santriyana, N., Dwimawati, E., & Listyandini, R. (2023). Faktor-Faktor yang Berhubungan dengan Kelelahan Kerja pada Pekerja Pembuat Bolu Talas Kujang di Home Industry Kelurahan Bubulak Tahun 2022. Promotor: Jurnal Mahasiswa Kesehatan Masyarakat, 6(4), 2–9. https://doi.org/10.32832/pro.v6i4.273
Shur, N. F., Creedon, L., Skirrow, S., Atherton, P. J., MacDonald, I. A., Lund, J., & Greenhaff, P. L. (2021). Age-related changes in muscle architecture and metabolism in humans: the likely contribution of physical inactivity to age-related functional decline. Ageing Research Reviews, 68, 101344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2021.101344
Song, Z., Yang, Z., Song, F., Wu, Y., & Konietzky, H. (2022). Mechanical responses of freeze–thaw treated natural stone masonry subject to compressive variable amplitude fatigue loading: Insights from stiffness loss and constitutive characterization. Construction and Building Materials, 350, 128908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128908
Souchet, A. D., Lourdeaux, D., Pagani, A., & Rebenitsch, L. (2023). A narrative review of immersive virtual reality’s ergonomics and risks at the workplace: cybersickness, visual fatigue, muscular fatigue, acute stress, and mental overload. Virtual Reality, 27(1), 19-50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-022-00672-0
Völker, J., Koch, T. J., Wiegelmann, M., & Sonnentag, S. (2024). Mind the misalignment: The moderating role of daily social sleep lag in employees' recovery processes. Journal of Organizational Behavior. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.2777
Widiyanti, E., Karimuna, S. R., & Saptaputra, S. K. (2021). Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kelelahan Kerja Pada Operator Alat Angkat Angkut Di Pt Pelindo Iv Cabang Kendari. Jurnal Kesehatan Dan Keselamatan Kerja Universitas Halu Oleo, 1(2), 48–53. https://doi.org/10.37887/jk3-uho.v1i2.16585
Wilkinson, D., Piasecki, M., & Atherton, P. (2018). The age-related loss of skeletal muscle mass and function: Measurement and physiology of muscle fibre atrophy and muscle fibre loss in humans. Ageing Research Reviews, 47, 123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2018.07.005
Xia, Q., Guo, C., Li, Y., Liu, T., & Liu, J. (2023). Fatigue characteristics of ancient brick masonry under cyclic load. Construction and Building Materials, 400, 132653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.132653
Xing, X., Zhong, B., Luo, H., Rose, T., Li, J., & Antwi-Afari, M. F. (2020). Effects of physical fatigue on the induction of mental fatigue of construction workers: A pilot study based on a neurophysiological approach. Automation in Construction, 120, 103381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103381
Zhen, G., Fu, Y., Zhang, C., Ford, N. C., Wu, X., Wu, Q., & Guan, Y. (2022). Mechanisms of bone pain: Progress in research from bench to bedside. Bone Research, 10(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41413-022-00217-w
Copyright (c) 2024 Rizky Maharja, Tajuddin Tajuddin, Sitti Fatimah Rahmansyah, Andi Tenriola Fitri Kessi, Arni Juliani, Riadnin Maharja

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted to publish their work online in third parties as it can lead to wider dissemination of the work.




