Covid-19 Prevention Zonation with Geographic Information System Based on Health Protocols in Southeast Sulawesi
Abstract
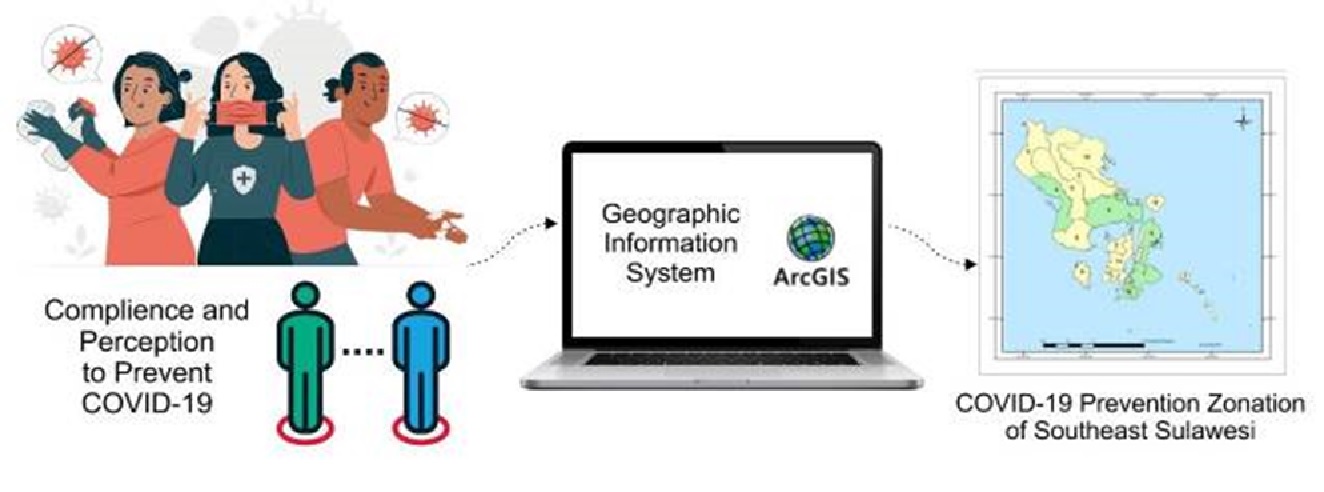
Efforts to prevent COVID-19 in Indonesia include the 3M movement. This movement is a COVID- 19 Task Force campaign to do 3M (Using masks, washing hands, and maintaining a safe distance) in preventing COVID-19. In relation to health protocols, it is necessary to review a person's desire to carry out or not carry out these preventive measures, this can be reviewed in the Health Belief Model theory. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the public often obtains information based on geographic information systems regarding the zoning of the development of COVID-19 in each region. Geographic Information System is the best medium for monitoring by mapping because it has a very good ability to visualize spatial data and its attributes. The purpose of this study is to find out the zoning of COVID-19 prevention in the 3M movement based on the Geographic Information System in the people of Southeast Sulawesi in 2020. This study uses a quantitative descriptive type of research. There is 17 districts/cities, there is no red zone on the variables of vulnerability, seriousness, benefits, barriers, health motivation, and cues to act, and only 1 region has good compliance (green zone) in prevention of COVID-19 through the 3M movement. An in- depth study of the variables studied with a more detailed methodology is needed so that the results obtained can complement each other to develope of science.
Downloads
References
Ainnurriza, U. S. (2020). Pemantauan Penyakit Demam Berdarah Dengue Dengan Sistem Informasi Geografis Di Kabupaten Sragen Tahun 2017-2019 [Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta]. http://eprints.ums.ac.id/81542/1/haldepanfix.pdf
Ali, F. S., Setiawan, & Ngadino. (2020). Hubungan Persepsi Dengan Perilaku Pencegahan Penularan Tuberkulosis Paru Di Puskesmas Perak Timur Tahun 2019. Gema Lingkungan Kesehatan, 18(1), 63–68. https://doi.org/10.36568/kesling.v18i1.1215
Apriaji, Y., Suwarni, L., Kesehatan, F. I., Pontianak, U. M., Pontianak, U. M., & Artikel, I. (2021). Determinan Perilaku Pencegahan Covid-19 Pada Jamaah Mesjid Kota Pontianak. 16(April), 14–19. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.26714/jkmi.16.1.2021.14-19
Aspan, S. H., Machfudloh, & Sutrisminah, E. (2020). Kepatuhan Masyarakat dalam Melakukan Pengobatan Bekam di Klinik Thibbunnabawi Darus Syifa. 6. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.30602/jkk.v6i2.521
Attamimy, H. B., & Qomaruddin, M. B. (2018). Aplikasi Health Belief Model Pada Perilaku Pencegahan Demam Berdarah Dengue. Jurnal PROMKES, 5(2), 245. https://doi.org/10.20473/jpk.v5.i2.2017.245-255
Dara, N., Saputri, T., Studi, P., Keperawatan, S., & Jayakarta, S. (2020). Hubungan antara Motivasi terhadap Perilaku Pencegahan Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) pada Pekerja Seks Komersial (PSK) di Lagoa Jakarta Utara Tahun 2019. Bionursing, 2(2), 75–85. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.20884/bion.v2i2.44
Ekowati, D., Udiyono, A., Martini, & Adi, M. S. (2017). Hubungan Pengetahuan Dengan Persepsi Mahasiswi Dalam Penerimaan Vaksinasi HPV Sebagai Upaya Pencegahan Kanker Serviks. Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat (E-Journal), 5(4), 334–341. https://ejournal3.undip.ac.id/index.php/jkm/article/view/18370
Ginting, T., Ladea, D., Kaban, B., & Ginting, R. (2021). Kepatuhan Pedagang Pasar Pagi dalam Melaksanakan Protokol Kesehatan Pencegahan Covid-19. Jurnal Prima Medika Sains, 03(1), 6–12. https://doi.org/10.34012/jpms.v3i1.1649
Husna, C. (2014). Upaya Pencegahan Kekambuhan Asma Bronchial Ditinjau dari Teori Health Belief Model di RSUDZA Banda Aceh. Idea Nursing Journal, 5(3), 75–89. http://www.jurnal.unsyiah.ac.id/INJ/article/download/6608/5409
Ihwatun, S., Ginandjar, P., Saraswati, L. D., & Udiyono, A. (2020). Faktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kepatuhan Pengobatan Pada Penderita Hipertensi Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Pudakpayung, Kota Semarang. Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat (E-Journal), 8(3), 352–359. https://ejournal3.undip.ac.id/index.php/jkm/article/view/26396
Jose, R., Narendran, M., Bindu, A., Beevi, N., Manju, L., & Benny, P. V. (2020). Public perception and preparedness for the pandemic Covid 19 : A Health Belief Model approach. Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, June, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cegh.2020.06.009
Juliati, L. (2020). Analisis Faktor Yang Memengaruhi Kepatuhan Perilaku Pencegahan Penularan Dan Kepatuhan Minum Obat Pada Pasien Tuberkulosis Paru Berbasis Teori Health Belief Model di Wilayah Puskesmas Surabaya. http://repository.unair.ac.id/97115/
Kasim, F., Satria, B., Wasliati, B., Sitepu, K., Nur Saputri, I., & Sihite, H. G. (2021). Faktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kepatuhan Masyarakat Terhadap Protokol Kesehatan Covid-19. Jurnal Kesmas Dan Gizi (Jkg), 3(2), 207–212. https://doi.org/10.35451/jkg.v3i2.687
Kementerian Kesehatan RI. (2020). Pedoman Pencegahan dan Pengendalian Coronavirus Disease (Covid-19).https://covid19.go.id/p/protokol/pedoman-pencegahan-dan-pengendalian-coronavirus-disease-Covid-19-revisi-ke-5
Lestari, R. A., Sari, C. W. M., & Kurniawan, T. (2018). Gambaran Persepsi Mahasiswa Terhadap Perilaku Pencegahan Diabetes Mellitus di Fakultas Keperawatan Universitas Padjadjaran. Jurnal Pendidikan Keperawatan Indonesia, 4(1), 60. https://doi.org/10.17509/jpki.v4i1.12345
Li, J. Bin, Yang, A., Dou, K., & Cheung, R. Y. M. (2020). Self-control moderates the association between perceived severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) and mental health problems among the Chinese public. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(13), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134820
Moudy, J., & Syakurah, R. A. (2020). Pengetahuan terkait usaha pencegahan Coronavirus Disease (Covid-19) di Indonesia. Higeia Journal of Public Health Research and Development, 4(3), 333–346. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.15294/higeia/v4i3/37844
Narsih, U., & Hikmawati, N. (2020). Pengaruh Persepsi Kerentanan Dan Persepsi Manfaat Terhadap Perilaku Remaja Putri Dalam Pencegahan Anemia. Indonesian Journal for Health Sciences, 4(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.24269/ijhs.v4i1.2328
Onoruoiza, S. I., Musa, A., Umar, B. D., & Kunle, Y. S. (2015). Using Health Belief Model as an Intervention to Non Compliance with Hypertension Information among Hypertensive Patient. International Organization of Scientific Research. Journal of Humanities and Social Science, 20(9), 11–16. https://doi.org/10.9790/0837-20951116
Prasetia, F. A. (2020). Pemerintah Ungkap Alasan Kampanyekan ’ Ingat Pesan Ibu ’ dalam Melawan Covid-. https://www.tribunnews.com/nasional/2020/10/01/pemerintah-ungkap-alasan-kampanyekan-ingat-pesan-ibu-dalam-melawan-Covid-19
Prihantini, W., Yunitasari, E., & Pradanie, R. (2017). Hubungan Perceived Benefit dan Perceived Barrier dengan Stadium Kanker Payudara Berdasarkan Teori Health Belief Model pada Pasien yang Berkunjung di POSA RSUD Dr . Soetomo. Idea Nursing Journal, 18–22. https://doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.20473/cmsnj.v7i1.12897
Riyadi, R., & Larasaty, P. (2021). Faktor Yang Berpengaruh Terhadap Kepatuhan Masyarakat Pada Protokol Kesehatan Dalam Mencegah Penyebaran Covid-19. Seminar Nasional Official Statistics, 2020(1), 45–54. https://doi.org/10.34123/semnasoffstat.v2020i1.431
Safri, F. M., Sukartini, T., & Ulfiana, E. (2019). Analisis Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kepatuhan Minum Obat Pasien Tb Paru Berdasarkan Health Belief Model Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Umbulsari, Kabupaten Jember. Indonesian Journal of Community Health Nursing, 2(2), 12–20. https://doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.20473/ijchn.v2i2.11904
Sarlinda. (2018). Pengaruh Penyuluhan Tentang Pentingnya Posyandu Lansia Menggunakan Leaflet Terhadap Peningkatan Pengetahuan dan Kunjungan Lansia di Posyandu Lansia Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Labibia Kota Kendari [Poltekes Kemenkes Kendari]. http://repository.poltekkes-kdi.ac.id/754/
Scarinci, I. C., Pandya, V. N., Kim, Y. il, Bae, S., Peral, S., Tipre, M., Hardy, C., Hansen, B., & Baskin, M. L. (2021). Factors Associated with Perceived Susceptibility to Covid-19 Among Urban and Rural Adults in Alabama. Journal of Community Health, 0123456789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10900-021-00976-3
Sulaksono, A. G. (2017). Pemanfaatan Aplikasi Sistem Informasi Geografis (SIG) untuk Pemetaan SMK KotaMalang. Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science (JOINTECS), 2(2). http://publishing-widyagama.ac.id/ejournal-v2/index.php/jointecs/article/view/475
Wiranti, Sriatmi, A., & Kusumastuti, W. (2020). Determinan Kepatuhan Masyarakat Kota Depok Terhadap Kebijakan Pembatasan Sosial Berskala Besar dalam Pencegahan Covid-19. Kebijakan Kesehatan Indonesia, 09(03), 117–124. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.22146/jkki.58484
Worldometer. (2020). Coronavirus Cases Info. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
Yunus, N. R., & Rezki, A. (2020). Kebijakan Pemberlakuan Lockdown Sebagai Antisipasi Penyebaran Corona Virus Covid-19. 7(3), 227–238. https://doi.org/10.15408/sjsbs.v7i3.15083
Copyright (c) 2022 Arum Dian Pratiwi, Wahyu Ishaq Trisnandi, Fifi Nirmala

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted to publish their work online in third parties as it can lead to wider dissemination of the work.






