Dietary Intake and Nutritional Status of Children in Kajang: A Study at An Indigenous Area in Indonesia
Abstract
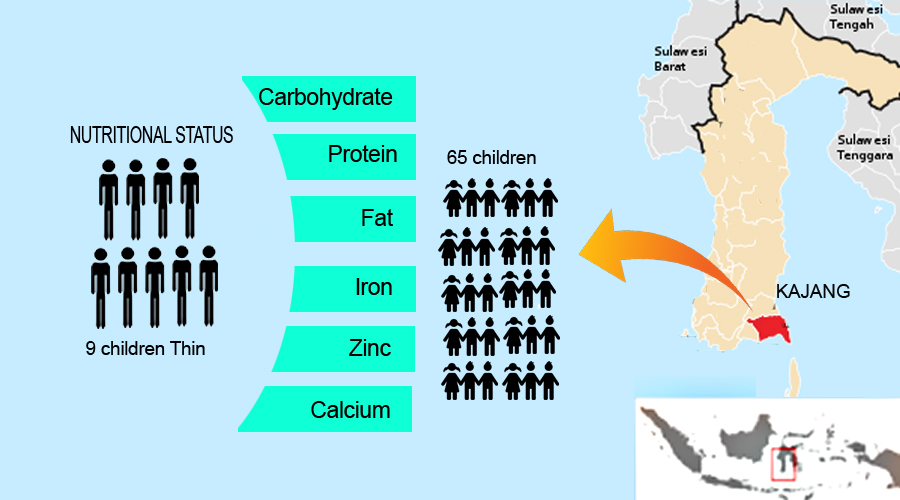
Malnutrition in children can contribute to growth limitations, and susceptibility to infection, which ultimately can inhibit the children’s growth and development. This study aimed to determine the fulfillment of macronutrient intake, micronutrient intake, and nutritional status of elementary school children at State Elementary School (hereafter SDN) Ammatoa Area, Kajang District, and Bulukumba Regency. This research was a descriptive study involving a population of 131 children and a sample of 65 children obtained by accidental sampling. The data were analyzed by using descriptive analysis of the percentage test. The results showed that the majority of macro-carbohydrate intakes (56.9%) were in the sufficient category, the majority of protein and fat (61.5% and 84.6%) were in the less category, while the intake of micronutrients, namely iron, zinc, and calcium primarily (83.1%, 80%, and 92.3%) in the less category, and the majority of nutritional status (86.2%) in the normal category. It was concluded that the intake of macro and micronutrients in elementary school children at the SDN Ammatoa region tended to be still lacking/low, despite their nutritional status, which tended to be normal. It is hoped that the relevant agencies will provide counselling to students regarding healthy and nutritious food by utilizing local food diversification in the Ammatoa customary area.
Downloads
References
Abbaspour, N., Hurrell, R., & Kelishadi, R. (2014). Review on iron and its importance for human health. Journal of research in medical sciences : the official journal of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, 19(2), 164-174. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3999603/
Abdollahi, M., Ajami, M., Abdollahi, Z., Kalantari, N., Houshiarrad, A., Fozouni, F., Mazandarani, F. S. (2019). Zinc supplementation is an effective and feasible strategy to prevent growth retardation in 6 to 24 month children: A pragmatic double blind, randomized trial. Heliyon, 5(11), e02581. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02581
Abrha, T., Girma, Y., Haile, K., Hailu, M., & Hailemariam, M. (2016). Prevalence and associated factors of clinical manifestations of vitamin a deficiency among preschool children in asgede-tsimbla rural district, north Ethiopia, a community based cross sectional study. Archives of Public Health, 74. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13690-016-0122-3
Akram, M., Munir, N., Daniyal, M., Egbuna, C., Găman, M. A., Onyekere, P. F., & Olatunde, A. (2020). Vitamins and Minerals: Types, sources and their functions. In Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals (pp. 149-172). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42319-3_9
Aliyah, D. P., Septriana, & Prasetyaningrum, Y. I. (2018). Status Gizi, Aktivitas Fisik, Dan Asupan Zat Gizi Makro Antara Siswa Sekolah Dasar Full Day Dan Half Day. Ilmu Gizi Indonesia, 2(1), 59-68. https://doi.org/10.35842/ilgi.v2i1.77
Amin, S. J. (2019). Talassa Kamase-Mase dan Zuhud: Titik Temu Kedekatan pada Tuhan dalam Bingkai Pasang Ri Kajang dan Ilmu Tasawuf. KURIOSITAS: Media Komunikasi Sosial dan Keagamaan, 12(1), 61-75. https://doi.org/10.35905/kur.v12i1.1199
Bergström, M., Håkansson, A., Blücher, A., & Andersson, H. S. (2020). From carbohydrates to fat: Trends in food intake among Swedish nutrition students from 2002 to 2017. PLOS ONE, 15(1), e0228200-e0228200. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0228200
Bird, J. K., Murphy, R. A., Ciappio, E. D., & McBurney, M. I. (2017). Risk of deficiency in multiple concurrent micronutrients in children and adults in the United States. Nutrients, 9(7), 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9070655
Bogale, T. Y., Bala, E. T., Tadesse, M., & Asamoah, B. O. (2018). Prevalence and associated factors for stunting among 6–12 years old school age children from rural community of Humbo district, Southern Ethiopia. BMC public health, 18(1), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5561-z
Colecraft, E., Owusu, J., Aryeetey, R., Vaccaro, J., & Huffman, F. (2017). Nutrition Intakes and Nutritional Status of School Age Children in Ghana. Journal of Food Research, 6, 11. https://dx.doi.org/10.5539/jfr.v6n2p11
Fiamanatillah, R. F., Ningtyias, F. W., & Rohmawati, N. (2019). Kontribusi Zat Gizi Makan Siang Sekolah Dan Kecukupan Gizi Terhadap Status Gizi Siswa Di Sd Al-Furqan Jember. Buletin Penelitian Sistem Kesehatan, 22(3), 265-271. https://doi.org/10.22435/hsr.v22i4.1297
Gombart, A. F., Pierre, A., & Maggini, S. (2020). A Review of Micronutrients and the Immune System-Working in Harmony to Reduce the Risk of Infection. Nutrients, 12(1), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010236
Gose, M., Krems, C., Heuer, T., & Hoffmann, I. (2016). Trends in food consumption and nutrient intake in Germany between 2006 and 2012: results of the German National Nutrition Monitoring (NEMONIT). British Journal of Nutrition, 115(8), 1498-1507. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114516000544
Hess, S. Y., Abbeddou, S., Jimenez, E. Y., Somé, J. W., Vosti, S. A., Ouédraogo, Z. P., & Brown, K. H. (2015). Small-quantity lipid-based nutrient supplements, regardless of their zinc content, increase growth and reduce the prevalence of stunting and wasting in young Burkinabe children: a cluster-randomized trial. PloS one, 10(3), e0122242. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122242
Hills, A. P., Dengel, D. R., & Lubans, D. R. (2015). Supporting public health priorities: recommendations for physical education and physical activity promotion in schools. Progress in cardiovascular diseases, 57(4), 368-374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2014.09.010
Kuhnlein, H. V. (2015). Food system sustainability for health and well-being of Indigenous Peoples. Public health nutrition, 18(13), 2415-2424. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980014002961
Lemke, S., & Delormier, T. (2017). Indigenous Peoples' food systems, nutrition, and gender: Conceptual and methodological considerations. Maternal & Child Nutrition, 13, e12499. https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.12499
Mesfin, F., Worku, A., & Berhane, Y. (2015). Prevalence and associated factors of stunting among primary school children in Eastern Ethiopia. Nutrition and Dietary Supplements, 7, 61. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDS.S80803
Mosby, I., & Galloway, T. (2017). “Hunger was never absent”: How residential school diets shaped current patterns of diabetes among Indigenous peoples in Canada. Cmaj, 189(32), E1043-E1045. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.170448
Naotunna, N. P. G. C. R., Dayarathna, M., Maheshi, H., Amarasinghe, G. S., Kithmini, V. S., Rathnayaka, M., & Agampodi, S. B. (2017). Nutritional status among primary school children in rural Sri Lanka; a public health challenge for a country with high child health standards. BMC public health, 17(1), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-016-4001-1
Oh, C., Keats, E. C., & Bhutta, Z. A. (2020). Vitamin and Mineral Supplementation During Pregnancy on Maternal, Birth, Child Health and Development Outcomes in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 12(2), 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020491
Omwami, E., Neumann, C., & Bwibo, N. (2011). Effects of a school feeding intervention on school attendance rates among elementary schoolchildren in rural Kenya. Nutrition (Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif.), 27, 188-193. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2010.01.009
Purwaningsih, K. A., Weta, I. W., & Aryani, P. (2019). Asupan Zat Gizi Dan Status Gizi Anak Vegetarian Dan Non Vegetarian Kelas 3-6 Sekolah Dasar di Bhaktivedanta Dharma School. E-Jurnal Medika Udayana(1), 23-26%V 28. https://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/eum/article/view/MU.2019.v8.I1.P4/
Rosela, E., Hastuti, T., & Triredjeki, H. (2017). Hubungan Status Gizi Dengan Perkembangan Anak Usia 1 Sampai 5 Tahun Di Kelurahan Tidar Utara, Kota Magelang Jurnal Keperawatan Soedirman (The Soedirman Journal of Nursing), 12(1), 27-37. http://dx.doi.org/10.20884/1.jks.2017.12.1.686
Rubio-López, N., Llopis-González, A., & Morales-Suárez-Varela, M. (2017). Calcium intake and nutritional adequacy in Spanish children: The ANIVA Study. Nutrients, 9(2), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9020170
Sheehy, T., Carey, E., Sharma, S., & Biadgilign, S. (2019). Trends in energy and nutrient supply in Ethiopia: a perspective from FAO food balance sheets. Nutrition Journal, 18(1), 46. http://doi.org/10.1186/s12937-019-0471-1
Tariku, E. Z., Abebe, G. A., Melketsedik, Z. A., & Gutema, B. T. (2018). Prevalence and factors associated with stunting and thinness among school-age children in Arba Minch Health and Demographic Surveillance Site, Southern Ethiopia. PloS one, 13(11), e0206659. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0206659
Taylor, C., Steer, C., Nicholas, Hays, N., & Emmett, P. (2019). Growth and body composition in children who are picky eaters: a longitudinal view. European journal of clinical nutrition, 73. http://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-018-0250-7
van Stuijvenberg, M. E., Nel, J., Schoeman, S. E., Lombard, C. J., du Plessis, L. M., & Dhansay, M. A. (2015). Low intake of calcium and vitamin D, but not zinc, iron or vitamin A, is associated with stunting in 2-to 5-year-old children. Nutrition, 31(6), 841-846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2014.12.011
Yazbeck, N., Hanna-Wakim, R., El Rafei, R., Barhoumi, A., Farra, C., Daher, R. T., & Majdalani, M. (2016). Dietary zinc intake and plasma zinc concentrations in children with short stature and failure to thrive. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism, 69(1), 9-14. https://doi.org/10.1159/000447648
Copyright (c) 2022 Fatmawaty Mallapiang, Andi Syamsiah Adha, Rini Jusriani

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted to publish their work online in third parties as it can lead to wider dissemination of the work.







