Tempeh and Carrots in A Brownies: Their Effects on Nutritional Status of Undernourished Students
Abstract
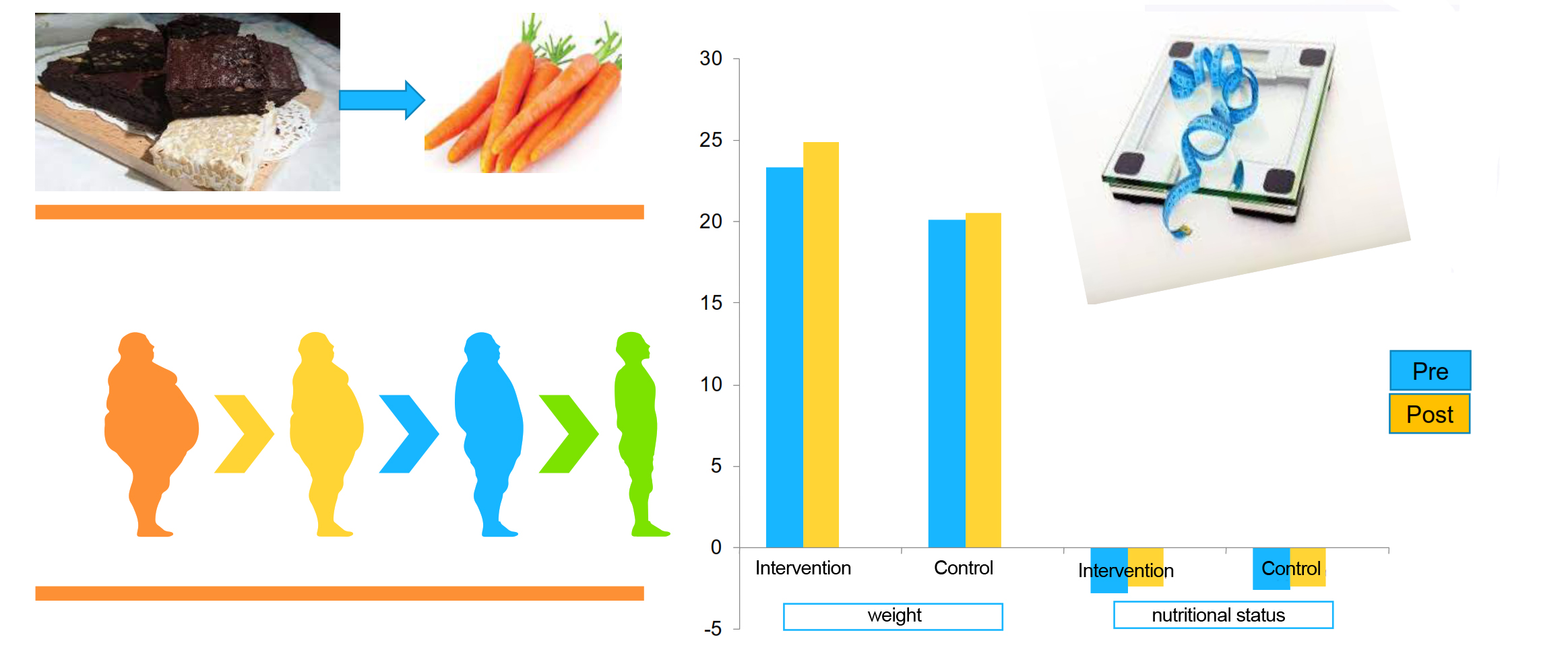
The role of nutrition is certainly needed to fulfill the growth process in school-age children because they are still in the growth phase. Whilst optimal growth and development depend on the provision of nutrients, both in terms of quality and quantity, that are considerably right. This study aimed to determine the effects of giving carrots and tempeh as the ingredients of brownies on the nutritional status of undernourished students at elementary school, Gowa Regency. This research was conducted through a quasi-experimental study with a non-randomized control group pretest-posttest design. The number of samples was as many as 24 people, with a sampling technique using purposive sampling. The method of analysis was a paired t-test. The results of this study indicated that there was an effect on nutritional status in the case group (p=0.001) and the control group (0.030,) and there was an effect on body weight in the case group (p=0.001) and the control group (p=0.028). However, providing tempeh brownies as a substitute for carrots and tempeh, brownies had not been able to change the nutritional status of undernourished students for 30 days which was indicated by the average z-score, which was still at <-2 SD. Further research is needed to be developed to determine the duration and efficient frequency of providing intervention in order to get optimal results. This study is expected to provide a new effort in presenting a combination of nutritious foods in an effort to overcome nutritional disorders among children.
Downloads
References
Branscum, P., & Sharma, M. (2014). Comparing the utility of the theory of planned behavior between boys and girls for predicting snack food consumption: implications for practice. Health Promotion Practice, 15(1), 134-140. https://doi.org/10.1177%2F1524839913481974
Bystrická, J., Kavalcová, P., Musilová, J., Vollmannová, A., Tomáš, T. Ó. T. H., & Lenková, M. (2015). Carrot (Daucus carota L. ssp. sativus (Hoffm.) Arcang.) as source of antioxidants. Acta agriculturae Slovenica, 105(2), 303-311. http://dx.doi.org/10.14720/aas.2015.105.2.13
Cotwright, C. J., Bales, D. W., Lee, J. S., Parrott, K., Celestin, N., & Olubajo, B. (2017). Like peas and carrots: Combining wellness policy implementation with classroom education for obesity prevention in the childcare setting. Public Health Reports, 132(2_suppl), 74S-80S. https://doi.org/10.1177%2F0033354917719706
Daru, J., Cooper, N. A., & Khan, K. S. (2016). Systematic review of randomized trials of the effect of iron supplementation on iron stores and oxygen carrying capacity in pregnancy. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica, 95(3), 270-279. https://doi.org/10.1111/aogs.12812
Elhadidy, G., Rizk, E., & El-Dreny, E. (2020). Improvement of Nutritional Value, Physical and Sensory Properties of Biscuits Using Quinoa, Naked Barley and Carrot. Egyptian Journal of Food Science, 48(1), 147-157. https://dx.doi.org/10.21608/ejfs.2020.27770.1050
Faidah, F. H., Moviana, Y., Isdiany, N., Surmita, S., & Hartini, P. W. (2019). Formulasi Makanan Enteral Berbasis Tepung Tempe Sebagai Alternatif Makanan Enteral Tinggi Protein. Jurnal Riset Kesehatan Poltekkes Depkes Bandung, 11(2), 67-74. https://doi.org/10.34011/juriskesbdg.v11i2.702
Farhadi, S., & Ovchinnikov, R. S. (2018). The relationship between nutrition and infectious diseases: A review. Biomedical and Biotechnology Research Journal (BBRJ), 2(3), 168. https://doi.org/10.4103/bbrj.bbrj_69_18
Fatmah, F. (2013). Intervensi biskuit tempe kurma bagi peningkatan status gizi balita penderita tuberkulosis. Jurnal Gizi Klinik Indonesia, 9(4), 147-154. https://doi.org/10.22146/ijcn.18361
Gallo, M., Ferrara, L., Calogero, A., Montesano, D., & Naviglio, D. (2020). Relationships between food and diseases: what to know to ensure food safety. Food Research International, 137, 109414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109414
Herring, C. M., Bazer, F. W., Johnson, G. A., & Wu, G. (2018). Impacts of maternal dietary protein intake on fetal survival, growth, and development. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 243(6), 525-533. https://doi.org/10.1177%2F1535370218758275
Hess, J., & Slavin, J. (2014). Snacking for a cause: nutritional insufficiencies and excesses of US children, a critical review of food consumption patterns and macronutrient and micronutrient intake of US children. Nutrients, 6(11), 4750-4759. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6114750
Ibeanu, V. N., Edeh, C. G., & Ani, P. N. (2020). Evidence-based strategy for prevention of hidden hunger among adolescents in a suburb of Nigeria. BMC public health, 20(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-09729-8
Iskandar, I. (2017). Pengaruh Pemberian Makanan Tambahan Modifikasi Terhadap Status Gizi Balita. AcTion: Aceh Nutrition Journal, 2(2), 120-125. http://dx.doi.org/10.30867/action.v2i2.65
Kementerian Kesehatan RI. (2013). Riset Kesehatan Dasar 2013. Jakarta: Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan
Kementerian Kesehatan RI. (2018). Hasil Pemantauan Status Gizi (PSG) Tahun 2017. Jakarta: Dirjen Kesehatan Masyarakat
Li, C., Zhu, N., Zeng, L., Dang, S., Zhou, J., & Yan, H. (2016). Effect of prenatal and postnatal malnutrition on intellectual functioning in early school-aged children in rural western China. Medicine, 95(31). https://doi.org/10.1097%2FMD.0000000000004161
Li, G., Fan, Y., Lai, Y., Han, T., Li, Z., Zhou, P., & Wu, J. (2020). Coronavirus infections and immune responses. Journal of medical virology, 92(4), 424-432. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25685
Miranti, M. G., & Wati, I. D. (2021, December). Nutritional Analysis of Non-Dairy Milk Almond-Tempeh as a Multivitamin Supplement for the Elderly. In International Joint Conference on Science and Engineering 2021 (IJCSE 2021) (pp. 137-142). Atlantis Press. https://dx.doi.org/10.2991/aer.k.211215.026
Norman, K., Haß, U., & Pirlich, M. (2021). Malnutrition in older adults—recent advances and remaining challenges. Nutrients, 13(8), 2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082764
Paramashanti, B. A., & Sulistyawati, S. (2019). Pengaruh integrasi intervensi gizi dan stimulasi tumbuh kembang terhadap peningkatan berat badan dan perkembangan balita kurus. Jurnal Gizi Klinik Indonesia, 15(1), 16-21. https://doi.org/10.22146/ijcn.31259
Permatasari, H. K., Nurkolis, F., Vivo, C. D., Noor, S. L., Rahmawati, R., Radu, S., & Nahdi, M. S. (2021). Sea grapes powder with addition of tempe rich in collagen: An anti-aging functional food. F1000Research, 10(789), 789. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.55307.2
Rytter, M. J. H., Kolte, L., Briend, A., Friis, H., & Christensen, V. B. (2014). The immune system in children with malnutrition—a systematic review. PloS one, 9(8), e105017. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0105017
Saputri, N. E., Hidayah, N., & Muttalib, Y. S. (2021). Komposisi Nilai Gizi Pempek Ikan Tenggiri (Scomberomorus Commersonii) Dengan Penambahan Wortel (Daucus Carota). Poltekita : Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan, 15(2), 143–149. https://doi.org/10.33860/jik.v15i2.488
Savarino, G., Corsello, A., & Corsello, G. (2021). Macronutrient balance and micronutrient amounts through growth and development. Italian Journal of Pediatrics, 47(1), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13052-021-01061-0
Singh, P., Kesharwani, R. K., & Keservani, R. K. (2017). Protein, carbohydrates, and fats: Energy metabolism. In Sustained Energy for Enhanced Human Functions and Activity (pp. 103-115). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-805413-0.00006-5
Ssentongo, P., Ba, D. M., Ssentongo, A. E., Fronterre, C., Whalen, A., Yang, Y., & Chinchilli, V. M. (2020). Association of vitamin A deficiency with early childhood stunting in Uganda: A population-based cross-sectional study. PLoS One, 15(5), e0233615. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0233615
Stodolak, B., Starzyńska-Janiszewska, A., Mika, M., & Wikiera, A. (2020). Rhizopus oligosporus and Lactobacillus plantarum Co-Fermentation as a Tool for Increasing the Antioxidant Potential of Grass Pea and Flaxseed Oil-Cake Tempe. Molecules, 25(20), 4759. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204759
Suriani, B., Sudirman, J., Mukarramah, S., Sabar, S., & Saleng, H. (2021). Fermented soybean cake nugget (tempeh) as an alternative for increasing weight of little children aged 36–60 months. Gaceta Sanitaria, 35, S382-S384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaceta.2021.10.056
Surman, S. L., Penkert, R. R., Sealy, R. E., Jones, B. G., Marion, T. N., Vogel, P., & Hurwitz, J. L. (2020). Consequences of vitamin A deficiency: immunoglobulin dysregulation, squamous cell metaplasia, infectious disease, and death. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(15), 5570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155570
Thomas, J. G., Bond, D. S., Phelan, S., Hill, J. O., & Wing, R. R. (2014). Weight-loss maintenance for 10 years in the National Weight Control Registry. American journal of preventive medicine, 46(1), 17-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2013.08.019
Wiseman, E. M., Bar-El Dadon, S., & Reifen, R. (2017). The vicious cycle of vitamin a deficiency: A review. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, 57(17), 3703-3714. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2016.1160362
World Health Organization (2015). World Health Statistic 2015. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/gho-documents/world-health-statistic-reports/world-health-statistics-2015.pdf
Copyright (c) 2022 Sukfitrianty Syahrir, Hurul Aini

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted to publish their work online in third parties as it can lead to wider dissemination of the work.







