Covid-19 Self-Isolation Telemedicine Service User Satisfaction in Indonesia
Abstract
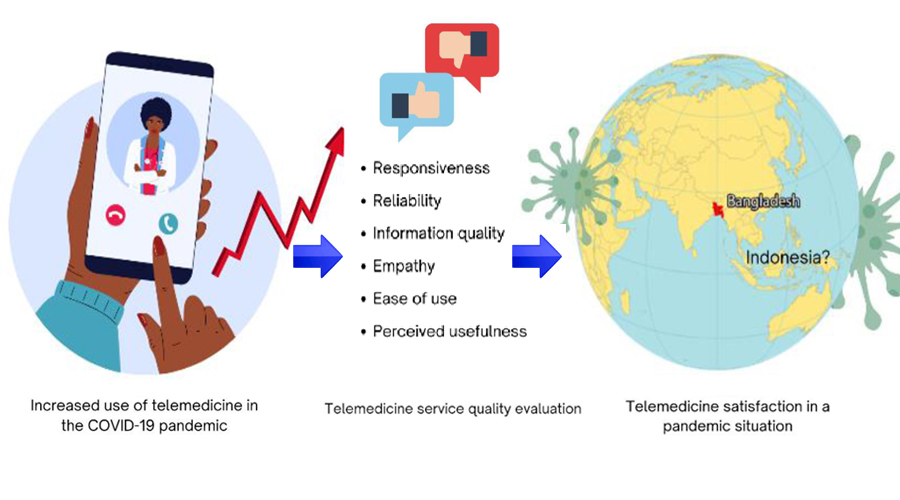
The Covid-19 Self-Isolation Telemedicine Service is established to reduce hospital occupancy rates amid peak Covid-19 cases. To develop better services, user satisfaction should be measured through service quality dimensions. This study aimed to determine the service quality dimensions of Indonesia's Covid-19 self-isolation telemedicine service. A cross-sectional design was utilized for this study. Out of 124,010 service users, data from a sample of 400 respondents were collected through online questionnaires. Service quality dimensions studied were responsiveness, reliability, information quality, empathy, ease of use, and perceived usefulness. Data were analyzed using the Spearman Rank correlation test. 91.7% of respondents were satisfied with the Covid-19 self-isolation telemedicine service. Responsiveness, reliability, information quality, empathy, ease of use, and perceived usefulness were correlated with user satisfaction, with the successive level of correlation (r): 0.474, 0.569, 0.485, 0.478, 0.569, and 0.478. All dimensions studied were correlated with user satisfaction at moderate and positive levels. However, few users were dissatisfied with the Covid-19 Self-Isolation Telemedicine Service. Several efforts are required to improve the service. This study provides new insights into telemedicine satisfaction in Indonesia because it analyzes the Covid-19 self-isolation telemedicine service provided by the Indonesian Ministry of Health for the first time.
Downloads
References
Aashima, Nanda, M., & Sharma, R. (2021). A review of patient satisfaction and experience with telemedicine: a virtual solution during and beyond COVID-19 pandemic. Telemedicine and e-Health, 27(12), 1325-1331. https://doi.org/10.1089/tmj.2020.0570
Aldekhyyel, R. N., Almulhem, J. A., & Binkheder, S. (2021, November). Usability of Telemedicine Mobile Applications during COVID-19 in Saudi Arabia: A Heuristic Evaluation of Patient User Interfaces. In Healthcare (Vol. 9, No. 11, p. 1574). MDPI. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9111574
Al-Samarraie, H., Ghazal, S., Alzahrani, A. I., & Moody, L. (2020). Telemedicine in Middle Eastern countries: Progress, barriers, and policy recommendations. International journal of medical informatics, 141, 104232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2020.104232
Busso, M., Gonzalez, M. P., & Scartascini, C. (2022). On the demand for telemedicine: Evidence from the COVID‐19 pandemic. Health Economics. 31(7), 1491–1505. https://doi.org/10.1002/hec.4523
Calton, B., Abedini, N., & Fratkin, M. (2020). Telemedicine in the time of coronavirus. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, 60(1), e12-e14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2020.03.019
Davies, N. G., Kucharski, A. J., Eggo, R. M., Gimma, A., Edmunds, W. J., Jombart, T., & Liu, Y. (2020). Effects of non-pharmaceutical interventions on COVID-19 cases, deaths, and demand for hospital services in the UK: a modelling study. The Lancet Public Health, 5(7), e375-e385. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30133-X
Gabrielsson-Järhult, F., Kjellström, S., & Josefsson, K. A. (2021). Telemedicine consultations with physicians in Swedish primary care: a mixed methods study of users’ experiences and care patterns. Scandinavian Journal of Primary Health Care, 39(2), 204-213. https://doi.org/10.1080/02813432.2021.1913904
Garcia, R., Olayele, A., & Han, W. (2017, January). Defining dimensions of patient satisfaction with telemedicine: An analysis of existing measurement instruments. In Proceedings of the 50th Hawaii international conference on system sciences. 3793–3802. https://doi.org/10.24251/hicss.2017.459
Handayani, P. W., Indriani, R., & Pinem, A. A. (2021). Mobile health readiness factors: From the perspectives of mobile health users in Indonesia. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, 24, 100590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2021.100590
Hoque, S. I., Karim, A. M., Hossen, R., & Arjumand, D. (2021). Evaluation of patients’ satisfaction in telemedicine service quality: a case study on Maizbhanderi Foundation, Fatikchari, Bangladesh. American Economic & Social Review, 8(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.46281/aesr.v8i1.1295
Indriyarti, E. R., & Wibowo, S. (2020). Bisnis Kesehatan Berbasis Digital: Intensi Pengguna Aplikasi Digital Halodoc. Jurnal Pengabdian Dan Kewirausahaan, 4(2). https://doi.org/10.30813/jpk.v4i2.2328
Kamal, S. A., Shafiq, M., & Kakria, P. (2020). Investigating acceptance of telemedicine services through an extended technology acceptance model (TAM). Technology in Society, 60, 101212.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2019.101212
Kaplan, B. (2020). Revisiting health information technology ethical, legal, and social issues and evaluation: telehealth/telemedicine and COVID-19. International journal of medical informatics, 143, 104239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2020.104239
Kapriani, K., & Ibrahim, I. (2022). Analisis Pengaruh Diskon dan Gratis Ongkos Kirim terhadap Keputusan Konsumen Menggunakan Layanan Jasa Grab Food pada Masa Pandemi. SEIKO: Journal of Management & Business, 5(2), 395-403. https://doi.org/10.37531/sejaman.v5i2.2050
Kementerian Kesehatan RI. (2022a). Layanan Telemedisin Isolasi Mandiri COVID-19. Kementerian Kesehatan RI. https://isoman.kemkes.go.id/
Kementerian Kesehatan RI. (2022b). Situasi Terkini Perkembangan Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). https://infeksiemerging.kemkes.go.id/
Kruse, C. S., Krowski, N., Rodriguez, B., Tran, L., Vela, J., & Brooks, M. (2017). Telehealth and patient satisfaction: a systematic review and narrative analysis. BMJ open, 7(8), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016242
Lu, W., Hou, H., Ma, R., Chen, H., Zhang, R., Cui, F., Zhang, Q., Gao, Y., Zhao, J., & Zhai, Y. (2021). Influencing factors of patient satisfaction in teleconsultation: A cross-sectional study. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 168, 120775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120775
Martinez, K. A., Rood, M., Jhangiani, N., Kou, L., Rose, S., Boissy, A., & Rothberg, M. B. (2018). Patterns of use and correlates of patient satisfaction with a large nationwide direct to consumer telemedicine service. Journal of general internal medicine, 33(10), 1768-1773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-018-4621-5
Monaghesh, E., & Hajizadeh, A. (2020). The role of telehealth during COVID-19 outbreak: a systematic review based on current evidence. BMC public health, 20(1), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-09301-4
Paramita, S. A., Yamazaki, C., Setiawati, E. P., & Koyama, H. (2018). Distribution trends of Indonesia's health care resources in the decentralization era. The International journal of health planning and management, 33(2), e586-e596. https://doi.org/10.1002/hpm.2506
Parmanto, B., Lewis Jr, A. N., Graham, K. M., & Bertolet, M. H. (2016). Development of the telehealth usability questionnaire (TUQ). International journal of telerehabilitation, 8(1), 3–10. https://doi.org/10.5195/ijt.2016.6196
Portnoy, J., Waller, M., & Elliott, T. (2020). Telemedicine in the era of COVID-19. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice, 8(5), 1489-1491. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaip.2020.03.008
Ramaswamy, A., Yu, M., Drangsholt, S., Ng, E., Culligan, P. J., Schlegel, P. N., & Hu, J. C. (2020). Patient satisfaction with telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic: retrospective cohort study. Journal of medical Internet research, 22(9), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.2196/20786
Sageena, G., Sharma, M., & Kapur, A. (2021). Evolution of smart healthcare: Telemedicine during COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India): Series B, 102(6), 1319-1324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-021-00568-8
Sari, G. G., & Wirman, W. (2021). Telemedicine sebagai Media Konsultasi Kesehatan di Masa Pandemic COVID 19 di Indonesia. Jurnal Komunikasi, 15(1), 43-54. https://doi.org/10.21107/ilkom.v15i1.10181
Sen-Crowe, B., Sutherland, M., McKenney, M., & Elkbuli, A. (2021). A closer look into global hospital beds capacity and resource shortages during the COVID-19 pandemic. journal of Surgical Research, 260, 56-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2020.11.062
Siboro, M. D., Surjoputro, A., & Budiyanti, R. T. (2021). Faktor-Faktor yang Mempengaruhi Penggunaan Layanan Telemedicine Pada Masa Pandemi COVID-19 di Pulau Jawa. Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat, 9(5), 613–620. https://doi.org/10.14710/jkm.v9i5.30762
Tantarto, T., Kusnadi, D., & Sukandar, H. (2020). Analysis of service quality towards patient satisfaction (comparative study of patients using telemedicine application and face to face consultation in healthcare). European Journal of Business and Management Research, 5(5). 1–7. https://doi.org/10.24018/ejbmr.2020.5.5.516
Ullhaque, A. D., Pratama, E. P. P. A., Rosmayani, P. A., Listiani, R., & Amalia, R. (2022). Hubungan Pelaksanaan Telemedicine Pada Kepuasan Pasien Saat Pandemi Covid-19: Systematic Review. Jurnal Kesehatan Tambusai, 3(2), 74-82. https://doi.org/10.31004/jkt.v3i2.4403
Vidal-Alaball, J., Acosta-Roja, R., PastorHernández, N., SanchezLuque, U., Morrison, D., NarejosPérez, S., Perez-Llano, J., Salvador Vèrges, A., & López Seguí, F. (2020). Telemedicine in the face of the COVID-19 pandemic. Atencion primaria, 52(6), 418-422.. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aprim.2020.04.003
Widuri, A., & Noor, H. Z. (2021). Upaya peningkatan layanan konsultasi kesehatan dengan telemedicine. JMM (Jurnal Masyarakat Mandiri), 5(4), 1194-1201. https://doi.org/10.31764/jmm.v5i4.5021
Copyright (c) 2022 Aulia Wulandari, Febrianti Febrianti

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted to publish their work online in third parties as it can lead to wider dissemination of the work.






