Infection of Soil-Transmitted Helminth among Mining Workers in Southeast Sulawesi
Abstract
Soil-Transmitted Helminth (hereafter STH) is considered as the leading cause of global health problems. This study aims to know the intensity and prevalence of STH infections among mining workers by comparing fecal and nail examinations in Morindino Village, Kambowa District, North Buton Regency Southeast Sulawesi Province. Feces were examined by using a native method, whilst the nails were observed by a sediment method. Additionally, descriptive and inferential analysis with independent t-tests were used to analyze the data. A total of 48 respondents were involved in this study. The observations of fecal respondents indicated that 4 (8.3%) of the respondents were infected with Ascaris lumbricoides, 12 (25%) had hookworm eggs, and 32 respondents (66.67%) were not infected. Moreover, the observation of STH worm eggs using nail samples showed that 1 respondent (2%) was infected with Ascaris lumbricoides, 4 (8.3%) respondents were infected by hookworm, and 43 respondents (89.58%) were free. The intensity of the attack was still in the mild category for all types of worm eggs; yet the highest attack was on hookworm for both examinations (2.16 and 2.25 eggs/individual). The research site took place around a sand mining land area with loose sandy soil structures that are protected from sunlight and mixed with humus to support the STH life cycle. Some individuals did open defecation habits at the research site leads to the STH contamination of the soil. Thus, the surveillance programs and infections control should be effectively implemented to manage worms incident.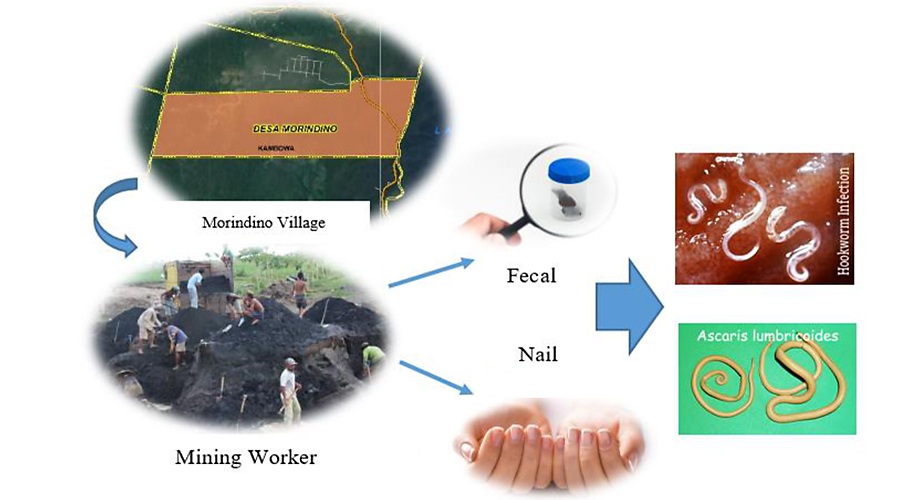
Downloads
References
Anwar, C., Annisa, S., Dalilah, D., & Novrikasari, N. (2018). The Relationship Between Soil Transmitted Helminthes (STH) Infection and Nutritional Status in Students of State Elementary School Number (SDN) 200 Palembang Indonesia. Bioscientia Medicina : Journal of Biomedicine and Translational Research, 2(2), 42–53. https://doi.org/10.32539/bsm.v2i2.39
Aram, S. A., Saalidong, B. M., Appiah, A., & Utip, I. B. (2021). Occupational health and safety in mining: Predictive probabilities of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) use among artisanal goldminers in Ghana. PLoS ONE, 16(9 September), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0257772
Baidowi, I. I., Armiyanti, Y., Febianti, Z., Nurdian, Y., & Hermansyah, B. (2019). The correlation between the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and Soil-Transmitted Helminths infection in the workers of Kaliputih Plantation Jember Regency. Journal of Agromedicine and Medical Sciences, 5(2), 61-68. https://doi.org/10.19184/ams.v5i2.9625
Buchmann, K., & Mehrdana, F. (2016). Effects of anisakid nematodes Anisakis simplex (sl), Pseudoterranova decipiens (sl) and Contracaecum osculatum (sl) on fish and consumer health. Food and Waterborne Parasitology, 4, 13-22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fawpar.2016.07.003
Bush, A. O., Lafferty, K. D., Lotz, J. M., & Shostak, A. W. (1997). Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. Journal of Parasitology, 83(4), 575–583. https://doi.org/10.2307/3284227
Dinas Kesehatan Kabupaten Buton (2021). Profil kesehatan Kabupaten Buton. Dinas Kesehatan Buton.
Cao, B., & Guiton, P. S. (2018). Important Human Parasites of the Tropics. Frontiers for Young Minds, 6(October), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/frym.2018.00058
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019). CDC - Ascariasis - Biology. http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ascariasis/biology.html
Chapman, P. R., Giacomin, P., Loukas, A., & McCarthy, J. S. (2021). Experimental human hookworm infection: a narrative historical review. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 15(12), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0009908
Clements, A. C. A., & Addis Alene, K. (2022). Global distribution of human hookworm species and differences in their morbidity effects: a systematic review. The Lancet Microbe, 3(1), e72–e79. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00181-6
Dhaka, R., Verma, R., , Aparna Parmar, V. C., , Meenakshi Kalhan, K. B., Chawla, S., , Ginni Agrawal, G. K., & Sachdeva, A. (2020). Association between the socioeconomic determinants and soil-transmitted helminthiasis among school-going children in a rural area of Haryana. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care, 9(7), 3712–3715. https://doi.org/10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc
Dunn, J. C., Turner, H. C., Tun, A., & Anderson, R. M. (2016). Epidemiological surveys of, and research on, soil-transmitted helminths in Southeast Asia: A systematic review. Parasites and Vectors, 9(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-016-1310-2
Eyayu, T., Yimer, G., Workineh, L., Tiruneh, T., Sema, M., Legese, B., Almaw, A., Solomon, Y., Malkamu, B., Chanie, E. S., Feleke, D. G., Jimma, M. S., Hassen, S., & Tesfaw, A. (2022). Prevalence, intensity of infection and associated risk factors of soil-transmitted helminth infections among school children at Tachgayint woreda, Northcentral Ethiopia. PLoS ONE, 17(4 April), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0266333
Hossain, M., & Bhuiyan, M. J. U. (2016). Hookworm Infection: A Neglected Tropical Disease of Mankind. Journal of Advanced Veterinary and Animal Research, 4(2), 24–43. https://doi.org/10.14737/journal.jimb/2016/4.2.24.43
Idris, O. A., Wintola, O. A., & Afolayan, A. J. (2019). Helminthiases; prevalence, transmission, host-parasite interactions, resistance to common synthetic drugs and treatment. Heliyon, 5(1), e01161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01161
Kementrian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. (2018). Laporan Nasional Riskesdas 2018. Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan. http://repository.litbang.kemkes.go.id/3514/
Khan, W., Rahman, H., Rafiq, N., Kabir, M., Ahmed, M. S., & Escalante, P. D. L. R. (2022). Risk factors associated with intestinal pathogenic parasites in schoolchildren. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 29(4), 2782–2786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.12.055
Kurscheid, J., Laksono, B., Park, M. J., Clements, A. C. A., Sadler, R., McCarthy, J. S., Nery, S. V., Soares-Magalhaes, R., Halton, K., Hadisaputro, S., Richardson, A., Indjein, L., Wangdi, K., Stewart, D. E., & Gray, D. J. (2020). Epidemiology of soil-transmitted helminth infections in semarang, central java, indonesia. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 14(12), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0008907
Lagatie, O., Verheyen, A., Van Hoof, K., Lauwers, D., Odiere, M. R., Vlaminck, J., Levecke, B., & Stuyver, L. J. (2020). Detection of ascaris lumbricoides infection by aba-1 coproantigen elisa. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 14(10), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0008807
Lim, M. D., Brooker, S. J., Belizario, V. Y., Gay-Andrieu, F., Gilleard, J., Levecke, B., van Lieshout, L., Medley, G. F., Mekonnen, Z., Mirams, G., Njenga, S. M., Odiere, M. R., Rudge, J. W., Stuyver, L., Vercruysse, J., Vlaminck, J., & Walson, J. L. (2018). Diagnostic tools for soil-transmitted helminths control and elimination programs: A pathway for diagnostic product development. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 12(3), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0006213
Mahartina, D., Mulyati, S., Soeharsono, S., & Hambal, M. (2020). Identification and Distribution of Soil Transmitted Helminths around The Shed and Grazing Fields of Madura Cattle in Sub-District of Geger, Bangkalan Regency. Journal of Parasite Science, 4(2), 49. https://doi.org/10.20473/jops.v4i2.29153
Muslimah, P. A. (2017). Faktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kejadian Infeksi Cacing Pada Pekerja Armada Mobil Sampah Di Kota Makassar. Journal Uin Alauddin, 11, 124–133. http://repositori.uin-alauddin.ac.id/16253/
Novikov, P. V., Malyshev, O. R., Lyssenko, K. A., & Kostyanovsky, R. G. (2008). Helminth infections: the great neglected tropical diseases. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 118(4), 1311–1321. https://doi.org/10.1070/MC2004v014n06ABEH002049
Paller, V. G. V., & Babia-Abion, S. (2019). Soil-transmitted helminth (STH) eggs contaminating soils in selected organic and conventional farms in the Philippines. Parasite Epidemiology and Control, 7, e00119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parepi.2019.e00119
Nasution, S. L. R., Nasution, A. N., Suhartomi, & Nasution, S. W. (2019). The Effect of Habits on Wearing Footwear and hand washing after playing on the ground Against Worms in Primary School Al-Wasliyah in Medan Deli. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1230(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1230/1/012049
Ross, A. G. P., Olveda, R. M., McManus, D. P., Harn, D. A., Chy, D., Li, Y., Tallo, V., & Ng, S. K. (2017). Risk factors for human helminthiases in rural Philippines. International Journal of Infectious Diseases, 54, 150–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2016.09.025
Steinbaum, L., Kwong, L. H., Ercumen, A., Negash, M. S., Lovely, A. J., Njenga, S. M., Boehm, A. B., Pickering, A. J., & Nelson, K. L. (2017). Detecting and enumerating soil-transmitted helminth eggs in soil: New method development and results from field testing in Kenya and Bangladesh. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 11(4), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0005522
Tadege, B., Mekonnen, Z., Dana, D., Sharew, B., Dereje, E., Loha, E., Verweij, J. J., Casaert, S., Vlaminck, J., Ayana, M., & Levecke, B. (2022). Assessment of environmental contamination with soil-transmitted helminths life stages at school compounds, households and open markets in Jimma Town, Ethiopia. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 16(4), 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0010307
Tuuk, H. A. V, Pijoh, V. D., & Bernadus, J. B. B. (2020). Survei Penyakit Kecacingan Pada Pekerja Tambang Tradisional di Desa Soyoan Kecamatan Ratatotok Kabupaten Minahasa Tenggara. Jurnal E-Biomedik, 8(1), 81–89. https://doi.org/10.35790/ebm.v8i1.28693
Vaz Nery, S., Clarke, N. E., Richardson, A., Traub, R., McCarthy, J. S., Gray, D. J., Vallely, A. J., Williams, G. M., Andrews, R. M., Campbell, S. J., & Clements, A. C. A. (2019). Risk factors for infection with soil-transmitted helminths during an integrated community level water, sanitation, and hygiene and deworming intervention in Timor-Leste. International Journal for Parasitology, 49(5), 389–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2018.12.006
World Health Organization. (2021). Soil-Transmitted Helminthiases (pp. 186–215). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-70841-1_5
Wikurendra, E. A., Crismiati, M., & Nurika, G. (2021). Relation of Parasites in Soil with The Existence of Parasites on Farmer’s Nails. Indonesian Journal of Medical Laboratory Science and Technology, 3(1), 47–55. https://doi.org/10.33086/ijmlst.v3i1.1850
Zeynudin, A., Degefa, T., Tesfaye, M., Suleman, S., Yesuf, E. A., Hajikelil, Z., Ali, S., Azam, K., Husen, A., Yasin, J., & Wieser, A. (2022). Prevalence and intensity of soil-Transmitted helminth infections and associated risk factors among household heads living in the peri-urban areas of Jimma town, Oromia, Ethiopia: A community-based cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE, 17(9 September), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0274702
Copyright (c) 2022 Yunita Amraeni, Muhammad Nirwan, Jumintono Suwardi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted to publish their work online in third parties as it can lead to wider dissemination of the work.






