Five-Finger Hypnosis and Murottal Therapy to Prevent Preeclampsia in Pregnant Women
Abstract
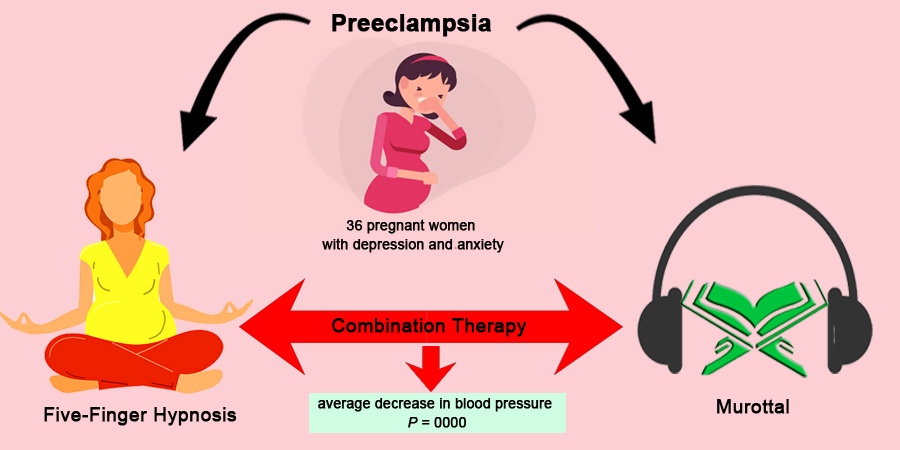
The incidence of preeclampsia in Indonesia for the Southeast Asian continent is relatively high, with roughly 190 per 100,000 live births. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the condition accounts for 12% of maternal deaths. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of Five-Finger hypnosis and murottal therapy in stabilizing blood pressure, pulse, respiration, and activating endorphins. The study employed a quantitative method, specifically a quasi-experimental one-group pre and post-test design. Univariate data analysis was conducted to examine the characteristics of the sample, including age, education, and parity, and the Wilcoxon test was employed as the statistical test. The results showed that pregnant women were at risk of developing preeclampsia, as indicated by the age, education level, and parity of 9, 14, and 24 pregnant women. Furthermore, a significant difference was observed between the pretest and posttest, with an average decrease in blood pressure ranging from 2 to 6 mmHg (p=0.000). This result study provided that five-Finger hypnosis intervention and murottal therapy were effective in preventing preeclampsia. Consequently, the study strongly recommended the dissemination of the Five-Finger and murottal hypnotic intervention modules to a wider population as a preventive measure against preeclampsia.
Downloads
References
Amelia, S., Kartika, I. R., & Apriliani, Y. (2022). Efektifitas Terapi Musik Klasik dan Murotal Al-Quran terhadap Penurunan Tekanan Darah Penderita Hipertensi. Media Karya Kesehatan, 5(1). https://doi.org/10.24198/mkk.v5i1.30310
Andriana, D. D., Utami, E. D., & Sholihat, N. K. (2018). Evaluasi penggunaan obat antihipertensi pada pasien pre-eklampsia rawat inap di RSUD Prof. Dr. Margono Soekarjo Purwokerto. Acta Pharmaciae Indonesia: Acta Pharm Indo, 6(1), 29-39. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3707186
Asmana, S. K., Syahredi, & Hilbertina, N. (2016). Hubungan Usia dan Paritas dengan Kejadian Preeklampsia Berat di Rumah Sakit Achmad Mochtar Bukittinggi Tahun 2012 - 2013. Jurnal Kesehatan Andalas, 5(3), 140–145. https://doi.org/10.25077/jka.v5i3.591
Azizah, L. M. R., Zainuri, I., & Akbar, A. (2023). The Effectivness of Five-Finger Hypnosis Theraphy to Decrease on Family’s Anxiety Levels in the Intensive Care Unit. Journal of Scientific Research, Education, and Technology (JSRET), 2(1), 42-52. https://doi.org/10.58526/jsret.v2i1.38
BAPPENAS. (2015). Rencana Pembangunan Jangka Menengah Indonesia 2015-2017.
Beevi, Z., Low, W. Y., & Hassan, J. (2019). The effectiveness of hypnosis intervention in alleviating postpartum psychological symptoms. American Journal of Clinical Hypnosis, 61(4), 409-425. https://doi.org/10.1080/00029157.2018.1538870
Bere, P. I. D. ., Sinaga, M., & Fernandez, H. . (2017). Risk Factors Pre-Eklamsia in Pregnant Mothers, Belu Regency. Media Kesehatan Masyarakat Indonesia, 13(2), 176-182. https://doi.org/10.30597/mkmi.v13i2.1992
Bilano, V. L., Ota, E., Ganchimeg, T., Mori, R., & Souza, J. P. (2014). Risk factors of pre-eclampsia/eclampsia and its adverse outcomes in low-and middle-income countries: a WHO secondary analysis. PloS one, 9(3), e91198. http://www.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0091198
Catsaros, S., & Wendland, J. (2020). Hypnosis-based interventions during pregnancy and childbirth and their impact on women's childbirth experience: A systematic review. Midwifery, 84, 102666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2020.102666
Dinas Kesehatan Provinsi Sulawesi Selatan. (2017). Profil Kesehatan Provinsi Sulawesi Selatan Tahun 2017. Dinkes Sulsel.
Domínguez-Solís, E., Lima-Serrano, M., & Lima-Rodriguez, J. S. (2021). Non-pharmacological interventions to reduce anxiety in pregnancy, labour and postpartum: A systematic review. Midwifery, 102, 103126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2021.103126
Endeshaw, M., Abebe, F., Bedimo, M., & Asart, A. (2015). Diet and pre-eclampsia: a prospective multicentre case–control study in Ethiopia. Midwifery, 31(6), 617-624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2015.03.003
Ertiana, D., & Wulan, S. R. (2019). Hubungan Usia dengan Kejadian Preeklamsia pada Ibu Hamil di RSUD Kabupaten Kediri Tahun 2018. Midwiferia Jurnal Kebidanan, 5(2), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.21070/mid.v5i2.2765
Fujianti, M. E. Y., Kristianto, H., & Yuliatun, L. (2023). Combination of Music Therapy and Murottal Therapy on Pain Level of Breast Cancer Patients. Jurnal Aisyah: Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan, 8(1), 405-414. http://dx.doi.org/10.30604/jika.v8i1.1649
Hanafusa, N., & Kopple, J. D. (2022). Nutrition and blood pressure. In Nutritional Management of Renal Disease (pp. 699-739). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818540-7.00010-0
Hapsari, S., & Puspitasari, D. (2021). Pengaruh Relaksasi Lima Jari Terhadap Tekanan Darah Penderita Chronic Kidney Disease. Jurnal Smart Keperawatan, 8(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.34310/jskp.v8i1.445
Hasnah. (2020). Modul Intervensi Keperawatan Pencegahan Pre Eklampsia pada Ibu Hamil (Rasdiyanah, N. F. Gani, Nurhidayah, N. K. Khotimah, Rasmawati, Ilhamsyah, & A. Adhiwijaya (eds.); I). Alauddin University Press. http://repositori.uin-alauddin.ac.id/18493/
Hill, A. M., McPhail, S. M., Wilson, J. M., & Berlach, R. G. (2017). Pregnant women’s awareness, knowledge and beliefs about pelvic floor muscles: a cross-sectional survey. International urogynecology journal, 28, 1557-1565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-017-3309-4
Hipni, R. (2019). Hubungan Paritas Dan Pendidikan Ibu Terhadap Kejadian Preeklampsia Di Rsud Idaman Banjarbaru. Embrio, 11(1), 23–29. https://doi.org/10.36456/embrio.vol11.no1.a1846
Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. (2019). Profil Kesehatan Indonesia Tahun 2019. Kementrian Kesehatan Repoblik Indonesia.
Khuzaiyah, S., Anies, & Wahyu, S. (2017). Efek Hipnosis Tehadap Perubahan Tekanan Darah Ibu Hamil Preeklampsia. Jurnal Siklus, 6(2), 212–217. http://dx.doi.org/10.30591/siklus.v6i2.582
Legrand, F., Grévin-Laroche, C., Josse, E., Polidori, G., Quinart, H., & Taïar, R. (2017). Effects of hypnosis during pregnancy: A psychophysiological study on maternal stress. Medical hypotheses, 102, 123-127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2017.03.026
Mahmood, S., Shah, K. U., Khan, T. M., Nawaz, S., Rashid, H., Baqar, S. W. A., & Kamran, S. (2019). Non-pharmacological management of hypertension: in the light of current research. Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971-), 188, 437-452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-018-1889-8
Mou, A. D., Barman, Z., Hasan, M., Miah, R., Hafsa, J. M., Das Trisha, A., & Ali, N. (2021). Prevalence of preeclampsia and the associated risk factors among pregnant women in Bangladesh. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-00839-w
Mulianda, N. D., & Umah, E. L. (2021). Penerapan Prosedur Terapi Relaksasi Benson Dan Murottal Al-Qur’an Surah Ar-Rahman Ayat 1-78 Terhadap Tekanan Darah Pada Pasien Hipertensi Primer Di RSUD Ungaran. Jurnal Ilmu Kedokteran dan Kesehatan Indonesia, 1(3), 12-27. https://doi.org/10.55606/jikki.v1i3.78
Nirupama, R., Divyashree, S., Janhavi, P., Muthukumar, S. P., & Ravindra, P. V. (2021). Preeclampsia: Pathophysiology and management. Journal of Gynecology Obstetrics and Human Reproduction, 50(2), 101975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jogoh.2020.101975
Novianti, H. (2016). Pengaruh Usia Dan Paritas Terhadap Kejadian Pre Eklampsia Di Rsud Sidoarjo. Jurnal Ilmiah Kesehatan, 9(1), 25–31. https://doi.org/10.33086/jhs.v9i1.180
Odigboegwu, O., Pan, L. J., & Chatterjee, P. (2018). Use of Antihypertensive Drugs During Preeclampsia. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, 5(May), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2018.00050
Part, C., le Roux, J., Chersich, M., Sawry, S., Filippi, V., Roos, N., Fairlie, L., Nakstad, B., de Bont, J., Ljungman, P., Stafoggia, M., Kovat, S., Luchters, S., & Hajat, S. (2022). Ambient temperature during pregnancy and risk of maternal hypertensive disorders: A time-to-event study in Johannesburg, South Africa. Environmental research, 212, 113596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113596
Rabinovich, A., Holtzman, K., Shoham-Vardi, I., Mazor, M., & Erez, O. (2019). Oligohydramnios is an independent risk factor for perinatal morbidity among women with pre-eclampsia who delivered preterm. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine, 32(11), 1776-1782. https://doi.org/10.1080/14767058.2017.1417377
Renault, K. M., Nørgaard, K., Nilas, L., Carlsen, E. M., Cortes, D., Pryds, O., & Secher, N. J. (2014). The Treatment of Obese Pregnant Women (TOP) study: a randomized controlled trial of the effect of physical activity intervention assessed by pedometer with or without dietary intervention in obese pregnant women. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology, 210(2), 134-e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2013.09.029
Tan, M. Y., Wright, D., Syngelaki, A., Akolekar, R., Cicero, S., Janga, D., Maclagan, W. K., Poon, L. C.. & Nicolaides, K. H. (2018). Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of early screening for pre‐eclampsia by NICE guidelines and a method combining maternal factors and biomarkers: results of SPREE. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology, 51(6), 743-750. https://doi.org/10.1002/uog.19039
Tanner, M. S., Davey, M. A., Mol, B. W., & Rolnik, D. L. (2022). The evolution of the diagnostic criteria of preeclampsia-eclampsia. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 226(2), S835-S843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2021.11.1371
Veftisia, V., & Khayati, Y. N. (2018). Hubungan Paritas Dan Pendidikan Ibu Dengan Kejadian Preeklampsia Di Wilayah Kabupaten Semarang. Jurnal SIKLUS, 07(2), 336–340. http://dx.doi.org/10.30591/siklus.v7i2.830
WHO. (2019a). Maternal ortality. 19 September 2019. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/maternal-mortality
WHO. (2019b). Trends in Maternal Mortality 2000 to 2017: Estimates by WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA, World Bank Group and the United Nations Population Division. World Health Organization. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/327596
Copyright (c) 2023 Hasnah Hasnah, Ilhamsyah Ilhamsyah, Darti Darti, Wahdaniah Wahdaniah, Nurul Fadhilah Gani, Nurhidayah Nurhidayah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted to publish their work online in third parties as it can lead to wider dissemination of the work.






