Positive Deviance Behavior Towards Stunting Prevention in Gunung Maddah Sampang Village
Abstract
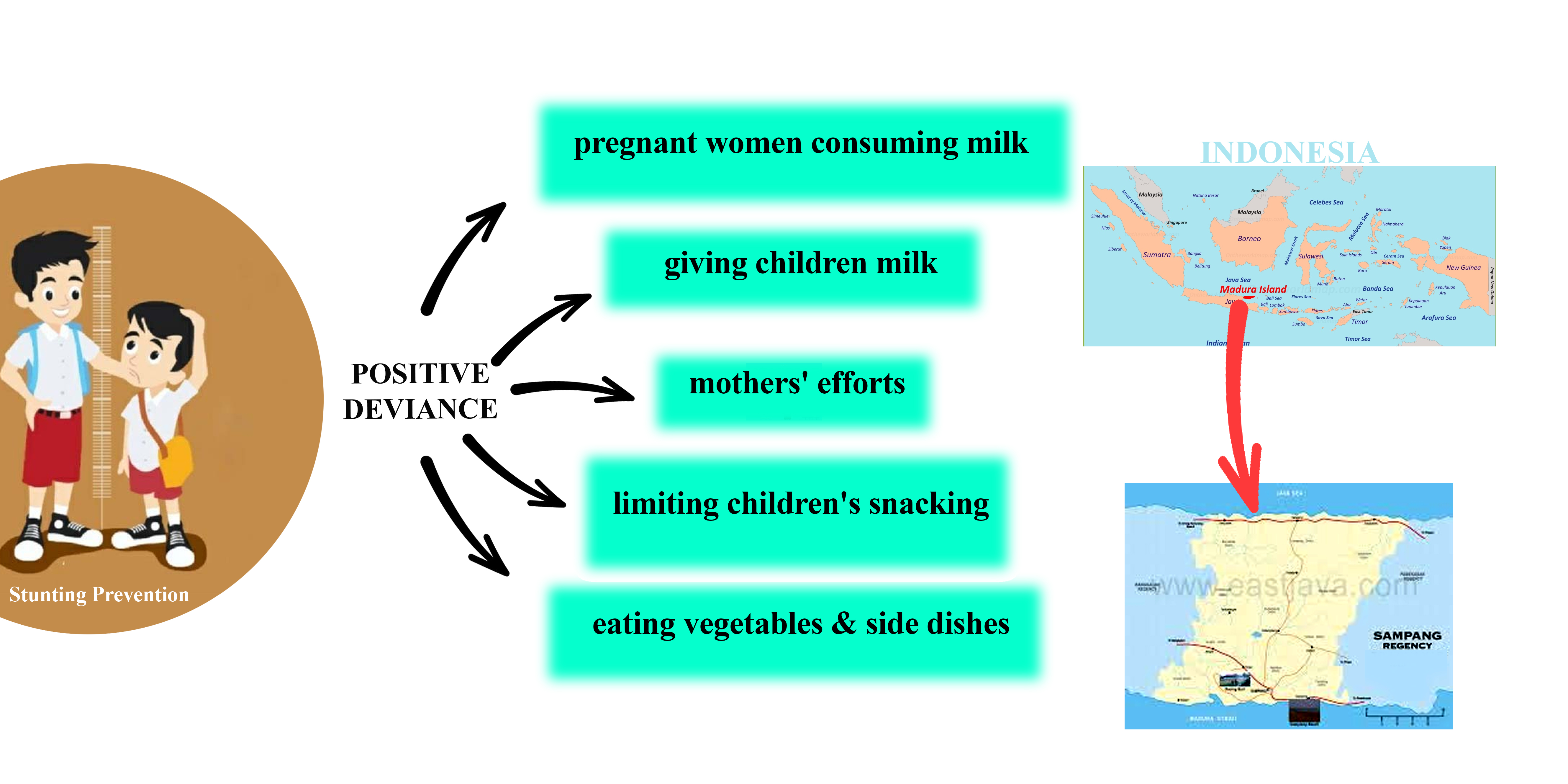
The high prevalence of stunting is a major nutritional problem that must be resolved because it is a threat to the future of Indonesian children. One of the efforts to prevent stunting needs to be done by searching for solutions that can be practiced by the general public by applying positive deviance to improve behavior in fulfilling nutritional content in pregnant women and children. The purpose of this research is to identify and study positive deviance behavior to prevent stunting. The research method used is the qualitative method. The research was conducted for 28 months (February 2020-June 2022) in Gunung Maddah Village, Sampang Regency, Madura Island, East Java, Indonesia. Data collection techniques included the results of Focus Group Discussions (FGDs), in-depth interviews, and observations obtained from 55 informants including mothers of toddlers, parents/parents-in-law, community members, cadres, and health workers. Data analysis techniques included content analysis consisting of data preparation, data editing, and data cleaning. The results showed that positive deviance behavior to prevent stunting in Gunung Maddah Sampang Village included the consumption of milk by pregnant women, the provision of milk to children (breast milk and/or cow's milk), mothers' efforts to overcome eating difficulties, limiting and regulating children's snacking habits, and the consumption of rice with vegetables and side dishes.
Downloads
References
Achón, M., Úbeda, N., García-González, Á., Partearroyo, T., & Varela-Moreiras, G. (2019). Effects of milk and dairy product consumption on pregnancy and lactation outcomes: a systematic review. Advances in nutrition, 10, S74-S87. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmz009
Aksu, S. B., & Öztürk, G. Z. (2021). Evaluation of mothers’ opinions on appetite and body shape perception of their children. Public Health, 195, 126-131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2021.04.021
Alang, H., Kusnadi, J., Ardyati, T., & Suharjono, S. (2020). Karakteristik nutrisi susu kerbau belang Toraja, Makassar. ZOOTEC, 40(1), 308-315. https://doi.org/10.35792/zot.40.1.2020.27773
Bella, F. D. (2020). Pola Asuh Positive Deviance dan Kejadian Stunting Balita di Kota Palembang. Jurnal Kesehatan Vokasional, 4(4), 209-210. https://doi.org/10.22146/jkesvo.45725
Bella, F. D., Fajar, N. A., & Misnaniarti, M. (2020). Hubungan pola asuh dengan kejadian stunting balita dari keluarga miskin di Kota Palembang. Jurnal Gizi Indonesia (The Indonesian Journal of Nutrition), 8(1), 31-39. https://doi.org/10.14710/jgi.8.1.31-39
Bokilia, K. T., Aspatria, U., & Toy, S. M. (2021). Positive Deviance Status Gizi Balita pada Keluarga Miskin di Desa Oeltua Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Baumata Kabupaten Kupang. Media Kesehatan Masyarakat, 3(3), 302-311. https://doi.org/10.35508/mkm.v3i3.3668
De Onis, M., Borghi, E., Arimond, M., Webb, P., Croft, T., Saha, K., & Flores-Ayala, R. (2019). Prevalence thresholds for wasting, overweight and stunting in children under 5 years. Public health nutrition, 22(1), 175-179. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980018002434
Efendi, S., Sriyanah, N., Cahyani, A. S., Hikma, S., & Kiswati, K. (2021). Pentingnya pemberian ASI eksklusif untuk mencegah stunting pada anak. Idea Pengabdian Masyarakat, 1(02), 107-111.
Fadilah, S. N. N., Ningtyias, F. W., & Sulistiyani, S. (2020). Tinggi badan orang tua, pola asuh dan kejadian diare sebagai faktor risiko kejadian stunting pada balita di kabupaten Bondowoso. Ilmu Gizi Indonesia, 4(1), 2020. https://doi.org/10.35842/ilgi.v4i1.148
FAO, IFAD, UNICEF, WFP and WHO. (2018). The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2018. Building climate resilience for food security and nutrition. Rome, FAO. https://www.fao.org/3/I9553EN/i9553en.pdf
Femidio, M., & Muniroh, L. (2020). Perbedaan pola asuh dan tingkat kecukupan zat gizi pada balita stunting dan non-stunting di wilayah pesisir Kabupaten Probolinggo. Amerta Nutrition, 4(1), 49. https://doi.org/10.20473/amnt.v4i1.2020.49-57
Fitriahadi, E. (2018). Hubungan tinggi badan ibu dengan kejadian stunting pada balita usia 24 -59 bulan. Jurnal Kebidanan Dan Keperawatan Aisyiyah, 14(1), 15–24. https://doi.org/10.31101/jkk.545.
Fitriani, E. (2020). Faktor Positive Deviance Karakteristik Keluarga Miskin dengan Status Gizi Anak Usia 0-24 Bulan di Wilayah Kerja Puskemas Medan Amplas Tahun 2019. J Kesehat Ilm Indones, 5(2), 36-46. https://doi.org/10.51933/health.v5i2.295
Fitrotuzzaqiyah, I., & Rahayu, S. (2022). Implementasi Intervensi Spesifik Dalam Upaya Pencegahan Stunting Balita Di Desa Gambarsari Kecamatan Pagaden Kabupaten Subang. Journal of Nutrition College, 11(3), 236-247. https://doi.org/10.14710/jnc.v11i3.32165
Green, M., Hadihardjono, D. N., Pries, A. M., Izwardy, D., Zehner, E., & Huffman, S. L. (2019). High proportions of children under 3 years of age consume commercially produced snack foods and sugar‐sweetened beverages in Bandung City, Indonesia. Maternal & Child Nutrition, 15, e12764. https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.12764
Hess, J. M., Jonnalagadda, S. S., & Slavin, J. L. (2016). What is a snack, why do we snack, and how can we choose better snacks? A review of the definitions of snacking, motivations to snack, contributions to dietary intake, and recommendations for improvement. Advances in Nutrition, 7(3), 466-475. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.115.009571
Ilmiasih, R. (2020). Perbandingan konsumsi susu sapi dan susu olahan oleh ibu terhadap frekuensi regurgitasi pada bayi. Jurnal Keperawatan, 11(2), 161–169. https://doi.org/10.22219/jk.v11i2.12683
Inzaghi, E., Pampanini, V., Deodati, A., & Cianfarani, S. (2022). The effects of nutrition on linear growth. Nutrients, 14(9), 1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091752
Maris, I., & Radiansyah, M. R. (2021). Kajian pemanfaatan susu nabati sebagai pengganti susu hewani. Food Scientia. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 1(2), 103-116. https://doi.org/10.33830/fsj.v1i2.2064.2021
Merita, M., & Hesty, H. (2019). Positive Deviance Gizi Pada Keluarga Miskin Di Desa Baru, Sarolangun Jambi. Jurnal Ipteks Terapan, 13(1), 55-66. https://doi.org/10.22216/jit.2019.v13i1.1186
Ministry of Health RI. (2019). The Basic Health Research 2018. https://layanandata.kemkes.go.id/katalog-data/riskesdas/ketersediaan-data/riskesdas-2018
Nafista, U. F., Nurhaeni, N., & Waluyanti, F. T. (2023). Improvement in maternal knowledge, attitudes, and children’s weight with education on World Health Organization feeding recommendations. La Pediatria Medica e Chirurgica, 45(s1). https://doi.org/10.4081/pmc.2023.314
Raudhatusabrina, S., Sastramihardja, H. S., & Setiowulan, W. (2021). Hubungan Pola Konsumsi Kudapan dengan Stunting pada Anak Kelas 1-2 SDN 036 Ujungberung Kota Bandung. Jurnal Sari Pediatri, 23(2), 121-128. https://doi.org/10.14238/sp23.2.2021.121-8
Sinaga, E. W. (2021). Tingkat Pengetahuan Ibu Terhadap Pemberian Susu Formula Pada Bayi Usia 0–6 Bulan Di Lingkungan IX Kelurahan Bandar Selamat Kecamatan Medan Tembung. Jurnal Ilmiah Kebidanan Imelda. 7(2), 59–64. https://doi.org/10.52943/jikebi.v7i2.640
Srivastava, A., Gwande, K., Bhattacharya, S., & Singh, V. K. (2019). Impact of the positive deviance approach on breastfeeding practices among tribal pregnant women: a before–after intervention study. CHRISMED Journal of Health and Research, 6(4), 222-228. https://doi.org/10.4103/cjhr.cjhr_165_18
Sudigyo, D., Hidayat, A. A., Nirwantono, R., Rahutomo, R., Trinugroho, J. P., & Pardamean, B. (2023). Literature study of stunting supplementation in Indonesian utilizing text mining approach. Procedia Comput. Sci, 216(2022), 722-729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2022.12.189
Sultana, P., Rahman, M. M., & Akter, J. (2019). Correlates of stunting among under-five children in Bangladesh: a multilevel approach. BMC nutrition, 5, 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-019-0304-9
World Health Organization. (2018). Global Nutrition Targets 2025: Stunting policy brief. Geneva.
World Health Organization. (2021). Breastfeeding. https://www.who.int/health-topics/breastfeeding#tab=tab_1
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted to publish their work online in third parties as it can lead to wider dissemination of the work.






