The Effectiveness of Brisk Walking Intervention Through Comic Book Education on Self-Efficacy and HbA1c Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Rural Area at Takalar Regency
Abstract
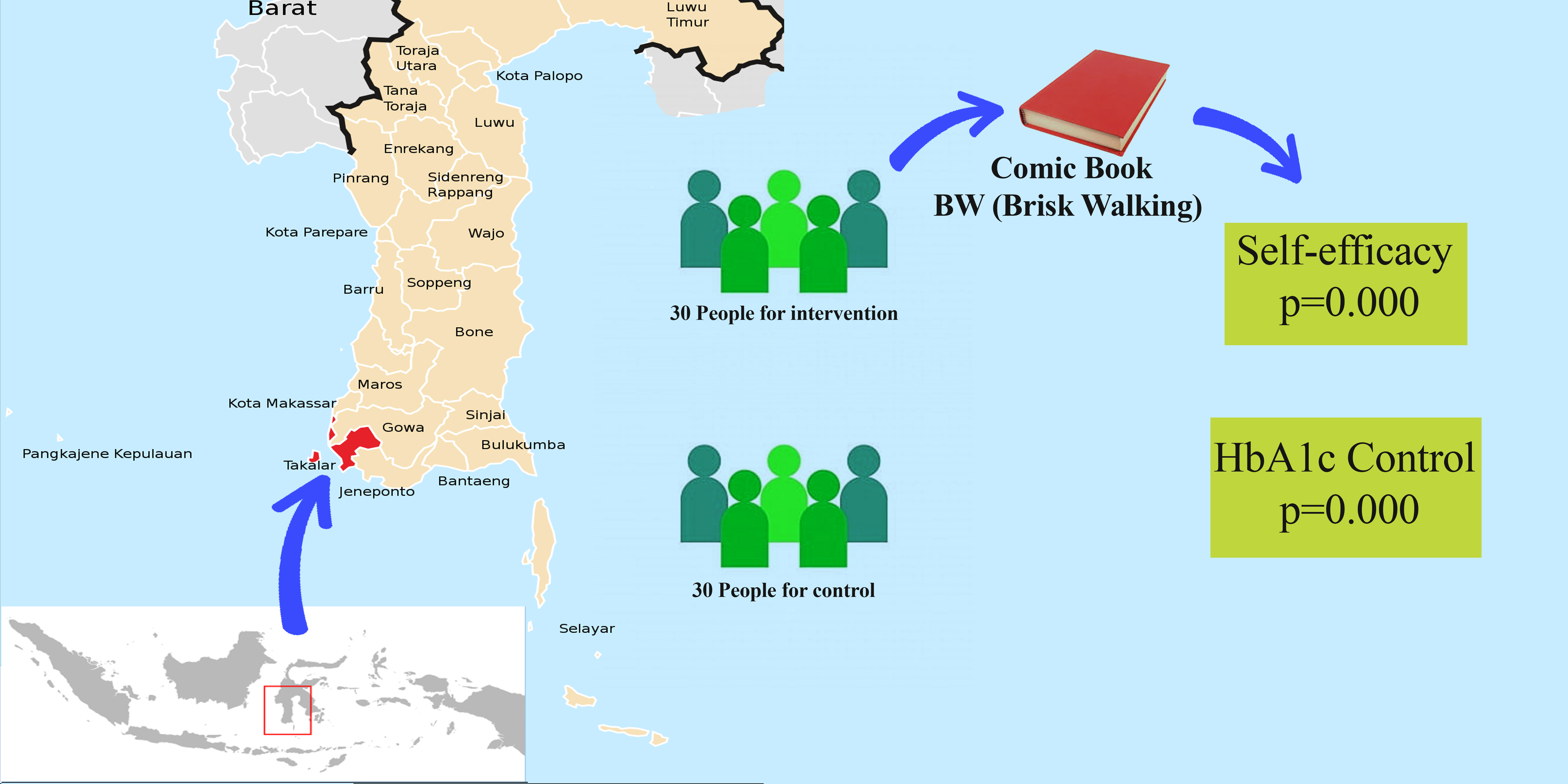
Poor self-efficacy and inability to control blood sugar (HbA1c) are special concerns in achieving structured self-management. Meanwhile, the use of educational media such as Comic book is a solution to improve the self-management of diabetes mellitus patients. Therefore, this research aimed to assess the effectiveness of comic book: BW (Brisk Walking) on self-efficacy and HbA1C control in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients in Takalar Regency. A quantitative method was used with a Quasi-Experimental two-group pre-post test design. The respondents were divided into two groups, namely Group 1 given comic Book: BW with WhatsApp Group monitoring, and Group 2 which received a similar intervention but without monitoring. A total of 60 respondents, 30 in each group were selected using the purposive sampling method, while data collection was carried out using the Exercise Self-Efficacy Scale (ESES) questionnaire consisting of 16 questions. Moreover, data analysis was conducted the T-test with a significance value of p<0.05. The results showed that the administration of comic book: BW significantly affected self-efficacy and HbA1c Control with p=0.000. BW caused a significant increase in self-efficacy and a decrease in HbA1c Control. This intervention has the potential to improve facilitate health workers and the patient self-management of type 2 diabetes mellitus through providing comic books.
Downloads
References
Abdullah, A. Z., Jafar, N., Syahrul, S., & Mallongi, A. (2023). Health Literacy Brisk Walking Exercise on Clinical Outcomes of Blood Sugar in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Indonesia. Pharmacognosy Journal, 15(2). http://dx.doi.org/10.5530/pj.2023.15.68
Almutairi, N., Hosseinzadeh, H., & Gopaldasani, V. (2020). The effectiveness of patient activation intervention on type 2 diabetes mellitus glycemic control and self-management behaviors: a systematic review of RCTs. Primary care diabetes, 14(1), 12-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcd.2019.08.009
Azami, G., Soh, K. L., Sazlina, S. G., Salmiah, M. S., Aazami, S., Mozafari, M., & Taghinejad, H. (2018). Effect of a nurse‐led diabetes self‐management education program on glycosylated hemoglobin among adults with type 2 diabetes. Journal of diabetes research, 2018(1), 4930157. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4930157
Bailey, R. A., Pfeifer, M., Shillington, A. C., Harshaw, Q., Funnell, M. M., VanWingen, J., & Col, N. (2015). Effect of a patient decision aid (PDA) for type 2 diabetes on knowledge, decisional self-efficacy, and decisional conflict. BMC health services research, 16, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-016-1262-4
Callaghan, T., Ferdinand, A. O., Akinlotan, M. A., Towne Jr, S. D., & Bolin, J. (2020). The changing landscape of diabetes mortality in the United States across region and rurality, 1999‐2016. The Journal of Rural Health, 36(3), 410-415. https://doi.org/10.1111/jrh.12354
Carbone, S., Del Buono, M. G., Ozemek, C., & Lavie, C. J. (2019). Obesity, risk of diabetes and role of physical activity, exercise training and cardiorespiratory fitness. Progress in cardiovascular diseases, 62(4), 327-333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2019.08.004
de Melo Ghisi, G. L., Aultman, C., Konidis, R., Foster, E., Tahsinul, A., Sandison, N., ... & Oh, P. (2020). Effectiveness of an education intervention associated with an exercise program in improving disease-related knowledge and health behaviours among diabetes patients. Patient Education and Counseling, 103(9), 1790-1797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2020.04.007
Health Office of Takalar District. (2022). Profil Penyakit Diabetes Melitus.
Erlina, L. (2020). Efikasi Diri dalam Meningkatkan Kemampuan Mobilisasi Pasien. Politeknik Kesehatan Kemenkes Bandung. https://repo.poltekkesbandung.ac.id/1643/
Gu, L., Wu, S., Zhao, S., Zhou, H., Zhang, S., Gao, M., & Tian, D. (2017). Association of social support and medication adherence in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. International journal of environmental research and public health, 14(12), 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14121522
Hakim, A. R., Wang, S. T., Widiantoro, F. X., Hannan, M., Wang, C. J., & Fetzer, S. J. (2020). The Indonesian version of the exercise self-efficacy scale: cross-cultural adaptation and psychometric testing. Asian Nursing Research, 14(5), 300-305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anr.2020.08.008
Hayati, K. (2021). Pengaruh Brisk Walking Exercise Terhadap Penurunan Kadar Gula Darah Pada Pasien DM Tipe II Di Rumah Sakit Grandmed Lubuk Pakam. Jurnal Penelitian Keperawatan Medik, 3(2), 23-29. https://doi.org/10.36656/jpkm.v3i2.660
He, L. I., Wei, W. R., & Can, Z. (2018). Effects of 12-week brisk walking training on exercise blood pressure in elderly patients with essential hypertension: a pilot study. Clinical and Experimental Hypertension, 40(7), 673-679. https://doi.org/10.1080/10641963.2018.1425416
International Diabetes Federation. (2021). IDF Diabetes Atlas. https://diabetesatlas.%0Aorg/
Jabardo-Camprubí, G., Donat-Roca, R., Sitjà-Rabert, M., Milà-Villarroel, R., & Bort-Roig, J. (2020). Drop-out ratio between moderate to high-intensity physical exercise treatment by patients with, or at risk of, type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Physiology & behavior, 215, 112786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2019.112786
Leung, A. Y., Leung, I. S., Liu, J. Y., Ting, S., & Lo, S. (2018). Improving health literacy and medication compliance through comic books: a quasi-experimental study of Chinese community-dwelling older adults. Global Health Promotion, 25(4), 67-78. https://doi.org/10.1177/1757975918798364
Li, J., Chattopadhyay, K., Xu, M., Chen, Y., Hu, F., Wang, X., & Li, L. (2019). Prevalence and predictors of polypharmacy prescription among type 2 diabetes patients at a tertiary care department in Ningbo, China: a retrospective database study. PLoS One, 14(7), e0220047. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0220047
Liu, J., Li, Q., Sun, X., Zhu, Z., & Xu, Y. (2023). Factors influencing programming self-efficacy: an empirical study in the context of Mainland China. Asia Pacific Journal of Education, 43(3), 835-849. https://doi.org/10.1080/02188791.2021.1985430
Lynch, E. B., Mack, L., Avery, E., Wang, Y., Dawar, R., Richardson, D., ... & Fogelfeld, L. (2019). Randomized trial of a lifestyle intervention for urban low-income African Americans with type 2 diabetes. Journal of general internal medicine, 34, 1174-1183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-019-04894-y
Ministry of Health RI. (2019). Laporan Nasional Riskesdas 2018. In Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan, Kementerian Kesehatan RI (Vol. 1, Issue 1). https://www.kemkes.go.id/article/view/19093000001/penyakit-jantung-penyebab-kematian-terbanyak-ke-2-di-indonesia.html
Park, S. H. (2015). Effects of passive static stretching on blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of physical therapy science, 27(5), 1463-1465. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.27.1463
Peleg-Raibstein, D. (2021). Understanding the link between maternal overnutrition, cardio-metabolic dysfunction and cognitive aging. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 15, 645569. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.645569
Ranasinghe, P., Jayawardena, R., Gamage, N., Sivanandam, N., & Misra, A. (2021). Prevalence and trends of the diabetes epidemic in urban and rural India: A pooled systematic review and meta-analysis of 1.7 million adults. Annals of epidemiology, 58, 128-148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annepidem.2021.02.01 .
Rodríguez, J. E., & Campbell, K. M. (2017). Racial and ethnic disparities in prevalence and care of patients with type 2 diabetes. Clinical Diabetes, 35(1), 66-70. https://doi.org/10.2337/cd15-0048
Seyedizadeh, S. H., Cheragh-Birjandi, S., & Hamedi Nia, M. R. (2020). The effects of combined exercise training (resistance‐aerobic) on serum kinesin and physical function in type 2 diabetes patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy (randomized controlled trials). Journal of diabetes research, 2020(1), 6978128. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6978128
Sobolesky, P. M., Smith, B. E., Saenger, A. K., Schulz, K., Apple, F. S., Scott, M. G., & Fitzgerald, R. L. (2018). Multicenter assessment of a hemoglobin A1c point-of-care device for diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Clinical Biochemistry, 61, 18-22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2018.09.007
Spencer, M. S., Kieffer, E. C., Sinco, B., Piatt, G., Palmisano, G., Hawkins, J., & Heisler, M. (2018). Outcomes at 18 months from a community health worker and peer leader diabetes self-management program for Latino adults. Diabetes care, 41(7), 1414-1422. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc17-0978
Swoboda, C. M., Miller, C. K., & Wills, C. E. (2017). Impact of a goal setting and decision support telephone coaching intervention on diet, psychosocial, and decision outcomes among people with type 2 diabetes. Patient education and counseling, 100(7), 1367-1373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2017.02.007
Wei, Y., Chen, Y., Zhao, Y., Rothman, R., Ming, J., Wang, L., & Xu, W. (2020). Health literacy and exercise interventions on clinical outcomes in Chinese patients with diabetes: a propensity score-matched comparison. BMJ Open Diabetes Research and Care, 8(1), e001179. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001179
Zainuddin, Z., Abdullah, A. Z., Jafar, N., Suriah S., Nursalam N., Darmawansyah D., Widiantoro X., & Irfandi, R. (2023). The application of social cognitive theory (SCT) to the mHealth diabetes physical activity (PA) app to control blood sugar levels of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients in Takalar regency. Journal of Public Health Research, 12(2), 22799036231172759. https://doi.org/10.1177/22799036231172759
Copyright (c) 2024 Zainuddin Zainuddin, Ernawati Ernawati, Yuniar Yuniar, Aswadi Aswadi, Gusti Pandi Liputo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted to publish their work online in third parties as it can lead to wider dissemination of the work.






