Sociodemographic, Infectious Diseases, Food Security, and Environmental Conditions in the Family of Children with and without Intraindividual Double Burden Malnutrition WaSt
Abstract
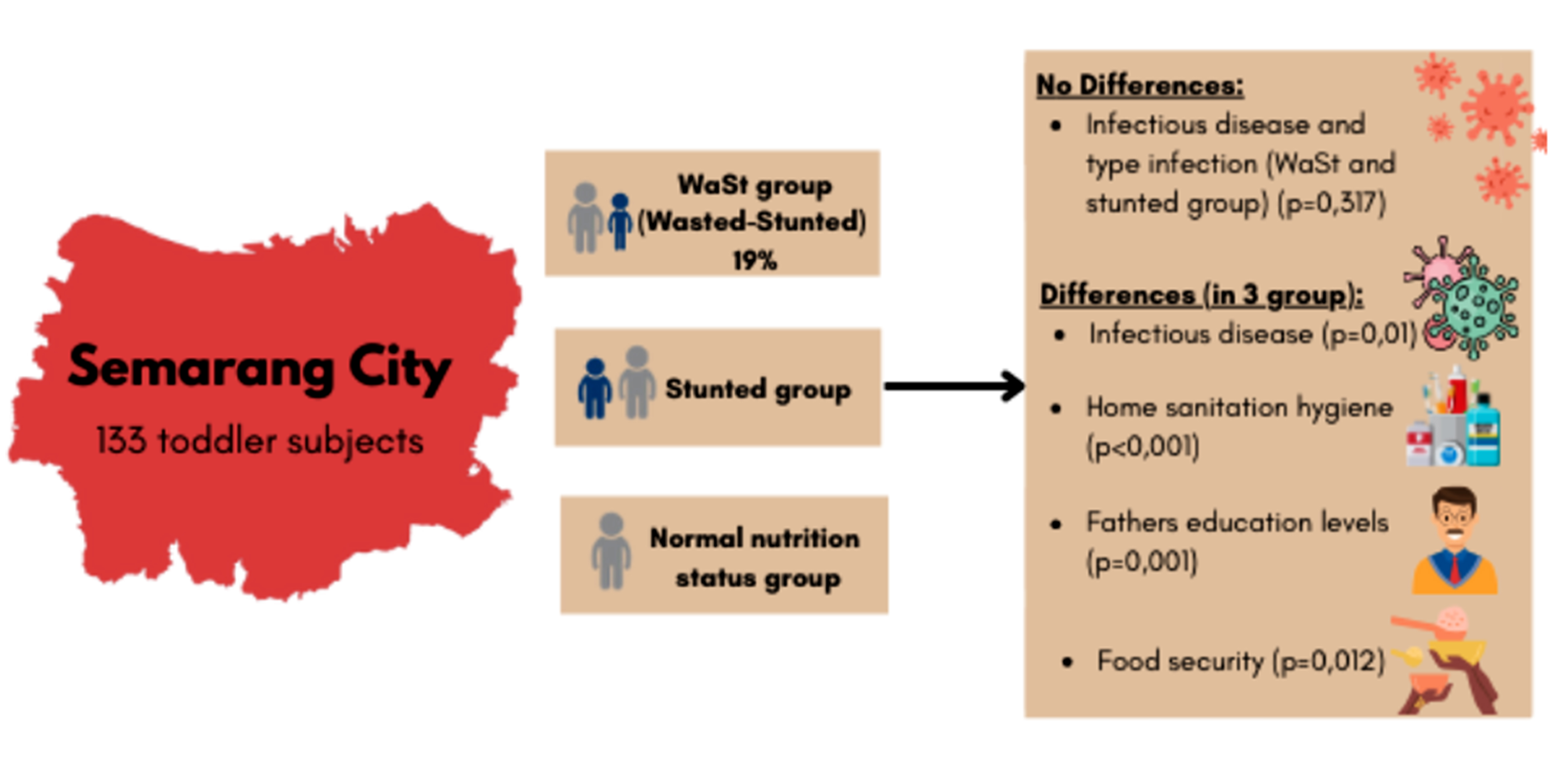
Intraindividual double-burden malnutrition, Wasted-Stunted (WaSt), frequently occurs in the same child simultaneously or at different moments throughout their life. This study aims to identify differences in the sociodemographic characteristics, incidence of infectious diseases, food security, and environmental conditions in the family of children with and without WaSt. The research employed a cross-sectional design conducted from April to October 2022 in Semarang City involving 133 subjects. The independent variables included toddler, mother, father, and family characteristics. The dependent variable was WaSt. The statistical tests used were the Kruskal-Wallis test with the Mann-Whitney U test for data that were not normally distributed and the one-way ANOVA test with the Bonferroni post hoc test for normally distributed data. This research shows that 19% of toddlers have WaSt. There were differences in the incidence of infectious diseases, home sanitation hygiene, father’s education, and food security between toddlers with normal nutritional status and the other two groups (stunted and WaSt) with a p-value <0.05. There were no differences in the incidence and types of infection between WaSt and stunted groups. Most family expenditures were allocated to food (70% in the WaSt and stunting groups and 60% in the normal nutritional status group). The government and related stakeholders need to pay more attention to families of children under five with limited access and facilities for hygiene and sanitation, low income, low parental education, and low food security to prevent an increase in the risk of WaSt.
Downloads
References
Aditianti, A., Raswanti, I., Sudikno, S., Izwardy, D., & Irianto, S. E. (2021). Prevalensi Dan Faktor Risiko Stunting Pada Balita 24-59 Bulan Di Indonesia: Analisis Data Riset Kesehatan Dasar 2018 [Prevalence and Stunting Risk Factors in Children 24-59 Months in Indonesia: Analysis of Basic Health Research Data 2018]. Penelitian Gizi Dan Makanan (The Journal of Nutrition and Food Research), 43(2), 51–64. https://doi.org/10.22435/pgm.v43i2.3862
Agustin, L., & Rahmawati, D. (2021). Hubungan Pendapatan Keluarga dengan Kejadian Stunting. Indonesian Journal of Midwifery (IJM), 4(1), 30–34. https://doi.org/10.35473/ijm.v4i1.715
Angood, C., Khara, T., Dolan, C., Berkley, J. A., Roberfroid, D., Seal, A., Kerac, M., Holland, D., Briend, A., McGrath, M., Hall, A., Mwangome, M., Bahwere, P., Moore, S., Myatt, M., Lelijveld, N., Golden, M., & Manary, M. (2016). Research priorities on the relationship between wasting and stunting. PLoS ONE, 11(5), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0153221
Astuti, N. F. W., Huriyati, E., & Susetyowati. (2020). The Prevalence and Determinants of Household Dual Burden Malnutrition in Indonesia. Media Kesehatan Masyarakat Indonesia, 16(1), 100–115. https://doi.org/10.30597/mkmi.v16i1.9064
Ayuningtyas, D., Hapsari, D., Rachmalina, R., Amir, V., Rachmawati, R., & Kusuma, D. (2022). Geographic and Socioeconomic Disparity in Child Undernutrition across 514 Districts in Indonesia. Nutrients, 14(4), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14040843
Brar, S., Akseer, N., Sall, M., Conway, K., Diouf, I., Everett, K., Islam, M., Sylmang Sène, P. I., Tasic, H., Wigle, J., & Bhutta, Z. (2020). Drivers of stunting reduction in Senegal: A country case study. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 112, 860S-874S. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqaa151
Briend, A., Khara, T., & Dolan, C. (2015). Wasting and stunting-similarities and differences: Policy and programmatic implications. Food and Nutrition Bulletin, 36(1), S15–S23. https://doi.org/10.1177/15648265150361S103
Budiastuti, I., & Rahfiludin, M. Z. (2019). Faktor risiko stunting pada anak di negara berkembang. Amerta Nutrition, 3(3), 122–129. https://doi.org/10.2473/amnt.v3i3.2019.122-129
Chilanga, E., & Chilanga, M. (2023). Predisposing and reinforcing factors of undernutrition among 0- to 59-months-old children in rural communities of central Malawi. Social Sciences and Humanities Open, 8(1), 100629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssaho.2023.100629
Demilew, Y. M. (2017). Factors associated with mothers’ knowledge on infant and young child feeding recommendation in slum areas of Bahir Dar City, Ethiopia: cross sectional study. BMC Research Notes, 10(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-017-2510-3
Dewi, P. L., & Kartini, A. (2017). Hubungan Pengetahuan Gizi, Aktivitas Fisik, Asupan Energi, dan Asupan Lemak dengan Kejadian Obesitas Pada Remaka Sekolah Menengah Pertama. Journal of Nutrition College, 6(3), 257–261.
Engle-stone, R., Guo, J., Ismaily, S., Addo, O. Y., Ahmed, T., & Oaks, B. (2020). Intraindividual double burden of overweight and micronutrient deficiencies or anemia among preschool children. 112, 478–487.
Géa-Horta, T., Silva, R. D. C. R., Fiaccone, R. L., Barreto, M. L., & Velásquez-Meléndez, G. (2016). Factors associated with nutritional outcomes in the mother-child dyad: A population-based cross-sectional study. Public Health Nutrition, 19(15), 2725–2733. https://doi.org/10.1017/S136898001600080X
Girma, F., Ayana, M., Abdissa, B., Aboma, M., Ketema, D., Kolola, T., & Wake, S. korsa. (2023). Determinants of under-five pneumonia among children visited in nine public health Hospitals in Ethiopia. Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, 24(August), 101441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cegh.2023.101441
Haddad, L., Cameron, L., & Barnett, I. (2015). The double burden of malnutrition in SE Asia and the Pacific: Priorities, policies and politics. Health Policy and Planning, 30(9), 1193–1206. https://doi.org/10.1093/heapol/czu110
Hawkes, C., Haddad, L., & Udomkesmalee, E. (2015). The global nutrition report 2015: What we need to do to advance progress in addressing malnutrition in all its forms. Public Health Nutrition, 18(17), 3067–3069. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980015003158
IFPRI. (2015). Global Nutrition Report 2015. https://globalnutritionreport.org/reports/2015-global-nutrition-report/
Jokhu, L. A., & Syauqy, A. (2024). Determinants of concurrent wasting and stunting among children 6 to 23 mo in Indonesia. Nutrition, 122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2024.112390
Karlsson, O., Kim, R., Joe, W., & Subramanian, S. V. (2020). SSM - Population Health The relationship of household assets and amenities with child health outcomes : An exploratory cross-sectional study in India 2015 – 2016. SSM - Population Health, 10, 100513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssmph.2019.100513
Krismanita, M. D., Triyanti1, Syafiq, A., & Sudiarti, T. (2022). Determinants of the Coexistence Dual Form of Malnutrition inPairs of Mother and Child Aged 6-59 Months in Bogor District. National Public Health Journal, 17(2), 129–135. https://doi.org/10.21109/kesmas.v17i2.5714
Lee, J., Houser, R., Must, A., Palma, P., & Bermudez, O. (2017). Association of the Familial Coexistence of Child Stunting and Maternal Overweight with Indigenous Women in Guatemala. Maternal and Child Health Journal, 21(11), 2102–2113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-017-2325-9
Li, S., Mohamed, N., & Ranjanee, S. (2024). Heliyon Social determinants of child malnutrition outcomes : Evidence from CHNS in China. 10(December 2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23887
Li, Z., Kim, R., Vollmer, S., & Subramanian, S. V. (2020). Factors Associated with Child Stunting, Wasting, and Underweight in 35 Low- And Middle-Income Countries. JAMA Network Open, 3(4), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.3386
Lu, W., Jenny, A., Romero, C., Diaz-artiga, A., Kuster, A., Canuz, E., Pillarisetti, A., Mccracken, J. P., Huang, W., Smith, K. R., Balmes, J., & Thompson, L. M. (2024). Biomass smoke exposure and somatic growth among children: The RESPIRE and CRECER prospective cohort studies in rural Guatemala. Environment International, 183(December 2023), 108401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2023.108401
Mahmudiono, T., Nindya, T. S., Andrias, D. R., Megatsari, H., & Rosenkranz, R. R. (2018). Household food insecurity as a predictor of stunted children and overweight/obese mothers (SCOWT) in urban Indonesia. Nutrients, 10(5), 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10050535
Methun, M. I. H., Kabir, A., Islam, S., Hossain, M. I., & Darda, M. A. (2021). A machine learning logistic classifier approach for identifying the determinants of Under-5 child morbidity in Bangladesh. Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, 12(April), 100812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cegh.2021.100812
Ministry of Health of Indonesia. (2023). Survei Kesehatan Indonesia (SKI) 2023 dalam Angka. Badan Kebijakan Pembangunan Kesehatan.
Mosli, H. H., Kutbi, H. A., Alhasan, A. H., & Mosli, R. H. (2020). Understanding the Interrelationship between Education, Income, and Obesity among Adults in Saudi Arabia. Obesity Facts, 13(1), 77–85. https://doi.org/10.1159/000505246
Mulatya, D. M., & Ochieng, C. (2020). Disease burden and risk factors of diarrhoea in children under five years: Evidence from Kenya’s demographic health survey 2014. International Journal of Infectious Diseases, 93, 359–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2020.02.003
Nurwitasari, A., & Wahyuni, C. U. (2015). Pengaruh status gizi dan riwayat kontak terhadap kejadian tuberkulosis anak di kabupaten jember. Jurnal berkala epidemiologi, 3(2), 158-169.. https://doi.org/10.20473/jbe.V3I22015.158-169
Pramudyat, S., Purbowati, & Pontang, G. S. (2017). Hubungan Karakteristik Ibu Dengan Stunting Pada Balita Usia 6-24 Bulan Didesa Gapura Kecamatan Pujut Kabupaten Lombok Tengah. 4(1), 1–9. http://repository2.unw.ac.id/1318/
Purnamasari, R. D., Sartika, R. A. D., & Sudarti, T. (2022). Current Intake and Infection Status were not Good Predictive Factors of Stunting among Children Aged 6-59 Months in Babakan Madang Sub-District, Bogor District, West Java, Indonesia. Indonesian Journal of Public Health Nutrition, 2(2), 41–48. https://doi.org/10.7454/ijphn.v2i2.5387
Purwanti, R., Syahadah, M. M., & Panunggal, B. (2022). Healthy Home Assesment Using Healthy Home Environmental Health Inspection Form. Jurnal Kesehatan Prima, 16(1), 25–33. https://doi.org/10.32.807/jkp.v16i2.799
Rachmah, Q., Mahmudiono, T., & Loh, S. P. (2021). Predictor of Obese Mothers and Stunted Children in the Same Roof: A Population-Based Study in the Urban Poor Setting Indonesia. Frontiers in Nutrition, 8(December), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.710588
Richard, S. A., Black, R. E., Gilman, R. H., Guerrant, R. L., Kang, G., Lanata, C. F., Mølbak, K., Rasmussen, Z. A., Sack, R. B., Valentiner-Branth, P., Checkley, W., Moore, S. R., Lima, A. A. M., Pinkerton, R. C., Aaby, P., Cabrera, L. Z., Bern, C., Sterling, C. R., Epstein, L. D., Verastegui, H. (2012). Wasting is associated with stunting in early childhood. Journal of Nutrition, 142(7), 1291–1296. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.111.154922
Sapartini, G., Wong, G. W. K., Indrati, A. R., Kartasasmita, C. B., & Setiabudiawan, B. (2022). Stunting as a Risk Factor for Asthma: The Role of Vitamin D, Leptin, IL-4, and CD23+. Medicina (Lithuania), 58(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58091236
Schoenbuchner, S. M., Dolan, C., Mwangome, M., Hall, A., Richard, S. A., Wells, J. C., Khara, T., Sonko, B., Prentice, A. M., & Moore, S. E. (2019). The relationship between wasting and stunting: A retrospective cohort analysis of longitudinal data in Gambian children from 1976 to 2016. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 110(2), 498–507. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqy326
Shamah-Levy, T., Mundo-Rosas, V., & A Rivera-Dommarco, J. (2014). Magnitude of food insecurity in Mexico: its relationship with nutritional status and socioeconomic factors. Salud Publica Mex, 56(1), 79–85. https://doi.org/10.21149/spm.v56s1.5169
Shamah-Levy, T., Mundo-Rosas, V., Morales-Ruan, C., Cuevas-Nasu, L., Méndez-Gómez-Humarán, I., & Pérez-Escamilla, R. (2017). Food insecurity and maternal-child nutritional status in Mexico: Cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Survey 2012. BMJ Open, 7(7), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014371
Shekar, M., Kakietek, J., Dayton Eberwein, J., & Walters, D. (2017). An Investment Framework for Nutrition: Reaching the Global Targets for Stunting, Anemia, Breastfeeding, and Wasting. 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1596/978-1-4648-1010-7
Sineke, J., Kawulusan, M., Purba, R. B., & Dolang, A. (2019). Hubungan Tingkat Pengetahuan Gizi Dan Pola Makan Dengan Kejadian Obesitas Pada Siswa Smk Negeri 1 Biaro. Jurnal GIZIDO, 11(01), 28–35. https://doi.org/10.47718/gizi.v11i01.752
Thurstans, S., Sessions, N., Dolan, C., Sadler, K., Cichon, B., Isanaka, S., Roberfroid, D., Stobaugh, H., Webb, P., & Khara, T. (2022). The relationship between wasting and stunting in young children: A systematic review. Maternal and Child Nutrition, 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.13246
Troeger, C. E., Khalil, I. A., Blacker, B. F., Biehl, M. H., Albertson, S. B., Zimsen, S. R. M., Rao, P. C., Abate, D., Ahmadi, A., Ahmed, M. L. C. Ibrahim, Akal, C. G., Alahdab, F., Alam, N., Alene, K. A., Alipour, V., Aljunid, S. M., Al-Raddadi, R. M., Alvis-Guzman, N., Amini, S., Reiner, R. C. (2020). Quantifying risks and interventions that have affected the burden of diarrhoea among children younger than 5 years: an analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 20(1), 37–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30401-3
UNICEF. (2019). Children, food and nutrition: Growing well in a changing world. https://www.unicef.org/media/63016/file/SOWC-2019.pdf
Wright, C. M., Macpherson, J., Bland, R., Ashorn, P., Zaman, S., & Ho, F. K. (2022). Wasting and Stunting in Infants and Young Children as Risk Factors for Subsequent Stunting or Mortality : Longitudinal Analysis of Data from Malawi , South Africa , and Pakistan. Journal of Nutrition, 151(7), 2022–2028. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxab054
Copyright (c) 2024 Rachma Purwanti, Novitasari Dwi Ajeng

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted to publish their work online in third parties as it can lead to wider dissemination of the work.






