Exploring Factors Influencing Diabetes Mellitus Incidence Among Participants of Chronic Disease Management Program in Rural Areas
Abstract
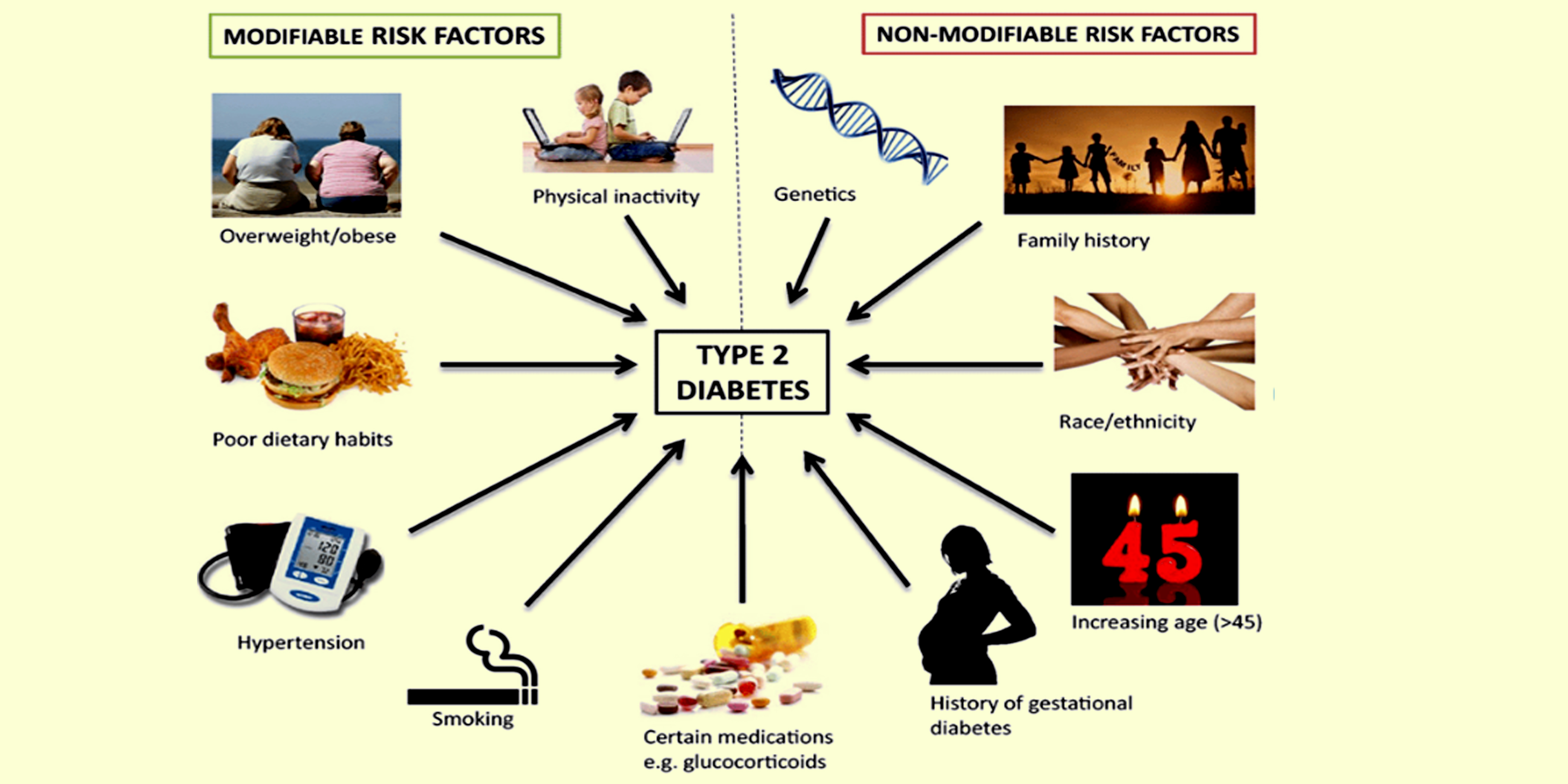
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic disease with an increasing global prevalence, including in Gorontalo Province, specifically type 2 DM (T2DM). Various risk factors, such as lifestyle, obesity, and lack of physical activity have been reported to contribute to DM incidence. This shows the importance of developing more effective prevention and management strategies. Therefore, this study aimed to explore factors related to DM incidence among participants of Chronic Disease Management Program (Prolanis) in rural areas of Boalemo District, Gorontalo Province. A quantitative method was used with a cross-sectional approach on 300 participants who were selected through the purposive sampling method. Data were collected using questionnaires to measure physical activity, dietary patterns, and smoking habits. Meanwhile, body mass index (BMI) and blood glucose levels were measured anthropometrically and through blood sugar tests. The results showed that dietary patterns (carbohydrates (p=0.003), fats (p=0.00), and fiber (p=0.000)), smoking habits (p=0.016), BMI (p=0.039), age (p=0.00), genetic factors (p=0.00), and gender (p=0.00) were significantly associated with DM incidence, while physical activity (p=0.095) and protein intake (p=0.128) were not associated. In this context, dietary fiber intake was the strongest predictor with Odds Ratio (OR) value of 7.37. Based on the results, dietary fiber intake, smoking habits, BMI, and age had a significant influence as predictors of DM incidence. The implications for public health included the need to increase awareness of the importance of healthy dietary patterns, reduce smoking habits, and monitor BMI to control the prevalence and improve the overall welfare of rural community.
Downloads
References
Akter, S., Goto, A., & Mizoue, T. (2017). Smoking and the risk of type 2 diabetes in Japan: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of epidemiology, 27(12), 553-561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.je.2016.12.017
Altobelli, E., Angeletti, P. M., Profeta, V. F., & Petrocelli, R. (2020). Lifestyle risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus and national diabetes care systems in European countries. Nutrients, 12(9), 2806. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092806
American Diabetes Association. (2021). Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care, 44(Supplement 1), S1-S232. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc21-Sint
Artese, A., Stamford, B. A., & Moffatt, R. J. (2019). Cigarette smoking: an accessory to the development of insulin resistance. American journal of lifestyle medicine, 13(6), 602-605. https://doi.org/10.1177/1559827617726516
Cao, Y., Sheng, J., Zhang, D., Chen, L., Jiang, Y., Cheng, D., & Xu, X. (2023). The role of dietary fiber on preventing gestational diabetes mellitus in an at-risk group of high triglyceride-glucose index women: A randomized controlled trial. Endocrine, 82(3), 542-549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-023-03478-5
Chatterjee, S., Khunti, K., & Davies, M. J. (2017). Type 2 diabetes. The lancet, 389(10085), 2239-2251. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30058-2
Chen, Y. (2023). Analysis of the Relationship between Physical Activity and Type-II Diabetes Mellitus in China. Highlights in Science, Engineering and Technology, 36, 1481-1486. https://doi.org/10.54097/hset.v36i.6272
Cole, J. B., & Florez, J. C. (2020). Genetics of diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications. Nature reviews nephrology, 16(7), 377-390. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-020-0278-5
de Oliveira, S. G., dos Santos, L. L., da Silva, D. N., & da Silva, S. L. (2021). Exercícios físicos e diabetes mellitus: revisão. Brazilian Journal of Development, 7(1), 8837-8847. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv7n1-599
Galicia-Garcia, U., Benito-Vicente, A., Jebari, S., Larrea-Sebal, A., Siddiqi, H., Uribe, K. B., & Martín, C. (2020). Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(17), 6275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176275
Gao, L. (2022). A Study on the Relationship among Dietary Fiber Intake, Type 2 Diabetes, Microbiota and Immune System. Highlights in Science, Engineering and Technology, 19, 51-57. https://doi.org/10.54097/hset.v19i.2694
Guasch-Ferré, M., Hruby, A., Salas-Salvadó, J., Martínez-González, M. A., Sun, Q., Willett, W. C., & Hu, F. B. (2015). Olive oil consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes in US women. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 102(2), 479-486. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.115.112029
Guevara, A. P. H., McGowan, S. J., Kazantzis, M., Stallons, T. R., Sano, T., Mulder, N. L., & Kruit, J. K. (2021). Increased insulin sensitivity and diminished pancreatic beta-cell function in DNA repair deficient Ercc1d/− mice. Metabolism, 117, 154711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154711
Halim, M., & Halim, A. (2019). The effects of inflammation, aging and oxidative stress on the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus (type 2 diabetes). Diabetes & metabolic syndrome: clinical research & reviews, 13(2), 1165-1172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2019.01.040
Health Office of Bolaang Mongondow District. (2022). Laporan Tahunan Kesehatan 2021. https://dinkes.bolmong.go.id/laporan-tahunan-2021
Health Office of Gorontalo Province. (2022). Profil Kesehatan Provinsi Gorontalo 2021. https://dinkes.gorontalo.go.id/profil-kesehatan-2021
Irawan, Q. P., Utami, K. D., & Reski, S. (2022). Hubungan Indeks Massa Tubuh (IMT) dengan Kadar HbA1c pada Penderita Diabetes Mellitus Tipe II di Rumah Sakit Abdoel Wahab Sjahranie. Formosa Journal of Science and Technology, 1(5), 459-468. https://doi.org/10.55927/fjst.v1i5.1220
Irma, I., Suhadi, S., Yuniar, N., Harleli, H., & Kamrin, K. (2022). Indeks Massa Tubuh (IMT) dan Lingkar Lengan Atas (LiLA) sebagai Penentu Diabetes Mellitus Tipe 2. Jurnal Kesehatan, 13(2), 225-232. https://doi.org/10.26630/jk.v13i2.2848
Irma, R. (2019). Identifikasi faktor yang berhubungan dengan kejadian diabetes melitus di kabupaten konawe provinsi sulawesi tenggara. Health Information: Jurnal Penelitian, 11(2), 146-154. https://doi.org/10.36990/hijp.v11i2.139
Jiang, L., Chang, J., Ziogas, A., Deapen, D., Reynolds, P., Bernstein, L., & Anton–Culver, H. (2019). Secondhand smoke, obesity, and risk of type II diabetes among California teachers. Annals of epidemiology, 32, 35-42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annepidem.2019.01.011
Jin, F., Zhang, J., Shu, L., & Han, W. (2021). Association of dietary fiber intake with newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus in middle-aged Chinese population. Nutrition Journal, 20, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12937-021-00740-2
Kautzky-Willer, A., Harreiter, J., & Pacini, G. (2016). Sex and gender differences in risk, pathophysiology and complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrine reviews, 37(3), 278-316. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2015-1137
Kral, B. G., Becker, D. M., Yanek, L. R., Vaidya, D., Mathias, R. A., Becker, L. C., & Kalyani, R. R. (2019). The relationship of family history and risk of type 2 diabetes differs by ancestry. Diabetes & Metabolism, 45(3), 261-267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2018.05.004
Li, A. L., Peng, Q., Shao, Y. Q., Fang, X., & Zhang, Y. Y. (2021). The interaction on hypertension between family history and diabetes and other risk factors. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 4716. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-83589-z
Ligthart, S., van Herpt, T. T., Leening, M. J., Kavousi, M., Hofman, A., Stricker, B. H., & Dehghan, A. (2016). Lifetime risk of developing impaired glucose metabolism and eventual progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study. The lancet Diabetes & endocrinology, 4(1), 44-51. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00362-9
Liu, F., Chen, G., Huo, W., Wang, C., Liu, S., Li, N., & Xiang, H. (2019). Associations between long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environmental pollution, 252, 1235-1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.06.033
Lohmueller, K. E., Sparsø, T., Li, Q., Andersson, E., Korneliussen, T., Albrechtsen, A., & Pedersen, O. (2013). Whole-exome sequencing of 2,000 Danish individuals and the role of rare coding variants in type 2 diabetes. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 93(6), 1072-1086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.11.005
Manson, J. E., Skerrett, P. J., Greenland, P., & VanItallie, T. B. (2004). The escalating pandemics of obesity and sedentary lifestyle: a call to action for clinicians. Archives of internal medicine, 164(3), 249-258. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.164.3.249
Ministry of Health of Indonesia (2019). Laporan Nasional Riskesdas 2018. Jakarta: Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan. Retrieved from https://www.kemkes.go.id/resources/download/info-terkini/riskesdas-2018.pdf
Nuraini, H. Y., & Supriatna, R. (2019). Hubungan Pola Makan, Aktivitas Fisik dan Riwayat Penyakit Keluarga Terhadap Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2. Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan Masyarakat, 5(1), 5–14. https://doi.org/10.33221/jikm.v5i1.14
Ohkuma, T., Peters, S. A., & Woodward, M. (2018). Sex differences in the association between diabetes and cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 121 cohorts including 20 million individuals and one million events. Diabetologia, 61, 2140-2154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-018-4664-5
Pan, A., Wang, Y., Talaei, M., Hu, F. B., & Wu, T. (2015). Relation of active, passive, and quitting smoking with incident type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The lancet Diabetes & endocrinology, 3(12), 958-967. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00316-2
Rahman. R. S., Almomen F., Alajmi, A. A., Asiri, I., Basudan, S., Alenezi, M., Alabdulwahab, F., Al Shammari, S., Alabdulmohsen, M. (2021). Predictors and Associated Risk Factors of Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Healthcare Sciences, 2(6). http://dx.doi.org/10.52533/JOHS.2022.2603
Rehman, K., Haider, K., & Akash, M. S. H. (2021). Cigarette smoking and nicotine exposure contributes for aberrant insulin signaling and cardiometabolic disorders. European Journal of Pharmacology, 909, 174410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174410
Reynolds, A., Mann, J., Cummings, J., Winter, N., Mete, E., & Te Morenga, L. (2019). Carbohydrate quality and human health: a series of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. The Lancet, 393(10170), 434-445. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)31809-9
Schwingshackl, L., Hoffmann, G., Lampousi, A. M., Knüppel, S., Iqbal, K., Schwedhelm, C., & Boeing, H. (2017). Food groups and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. European journal of epidemiology, 32, 363-375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-017-0246-y
Sudrajat, A., Romadhona, M., Manurung, S., Suratun, S., Yardes, N., Lusiani, D., & Hartini, T. (2023). Relationship between family history, diet and sedentary behavior with the incidence of diabetes mellitus. Asian Journal of Dental and Health Sciences, 3(2), 26-31. https://doi.org/10.22270/ajdhs.v3i2.42
Suputra, I. G. L. R. D., & Budiyasa, D. G. A. (2023). Faktor Risiko Kejadian Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2 Pada Pasien Rawat Jalan Di RSUD Sanjiwani Gianyar. Herb-Medicine Journal: Terbitan Berkala Ilmiah Herbal, Kedokteran dan Kesehatan, 5(4), 23-27. https://dx.doi.org/10.30595/hmj.v5i4.17061
The InterAct Consortium. (2015). Dietary fibre and incidence of type 2 diabetes in eight European countries: the EPIC-InterAct Study and a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Diabetologia , 58, 1394–1408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-015-3585-9
Tursinawati, Y., Setiowati, L., Wahab, Z., & Kartikadewi, A. (2022). Korelasi Indeks Massa Tubuh dan Tekanan Darah dengan Rasio TG/HDL pada Penderita Diabetes Mellitus Tipe 2 Etnis Jawa: Correlation of Body Mass Index and Blood Pressure with TG/HDL Ratio in Type 2 Diabetes Javanese Patients. Medica Hospitalia: Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(3), 335-339. https://doi.org/10.36408/mhjcm.v9i3.817
Veridiana, N. N., & Nurjana, M. A. (2019). Hubungan Perilaku Konsumsi dan Aktivitas Fisik dengan Diabetes Mellitus di Indonesia. Buletin Penelitian Kesehatan, 47(2), 97-106. https://doi.org/10.22435/bpk.v47i2.667
Wang, T., Zhao, Z., Wang, G., Li, Q., Xu, Y., Li, M., & Wang, W. (2021). Age-related disparities in diabetes risk attributable to modifiable risk factor profiles in Chinese adults: a nationwide, population-based, cohort study. The Lancet Healthy Longevity, 2(10), e618-e628. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2666-7568(21)00177-X
World Health Organization. (2020). Global report on diabetes. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/diabetes/global-report/en/
World Health Organization. (2022). Global status report on physical activity 2022. World Health Organization.
Xu, Q., Tao, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, X., Xue, C., & Liu, Y. (2021). Dietary fiber intake, dietary glycemic load, and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus during the second trimester: A nested case-control study. Asia Pacific journal of clinical nutrition, 30(3), 477-486. doi: https://doi.org/10.6133/APJCN.202109_30(3).0014
Yan, Y., Wu, T., Zhang, M., Li, C., Liu, Q., & Li, F. (2022). Prevalence, awareness and control of type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk factors in Chinese elderly population. BMC Public Health, 22(1), 1382. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-13759-9
Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, S., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, Q. (2023). Complex Association Among Diet Styles, Sleep Patterns, and Obesity in Patients with Diabetes. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity, 749-767.
Zhou, B., Lu, Y., Hajifathalian, K., Bentham, J., Di Cesare, M., Danaei, G., Bixby, H., Cowan, M., Ali, M., Taddei, C., Lo, W., Reis-Santos, B., Stevens, G., Riley, L., Miranda, J., Bjerregaard, P., Rivera, J., Fouad, H., Ma, G., Zuñiga Cisneros, J. (2016). Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: a pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4·4 million participants. The Lancet, 387(10027), 1513–1530. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(16)00618-8
Copyright (c) 2024 Syamsul Alam, Dian Rezki Wijaya, Agil Kurniawan, Maesarah Maesarah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted to publish their work online in third parties as it can lead to wider dissemination of the work.






