Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus and Awareness of Its Management among Tailors in Urban India
Abstract
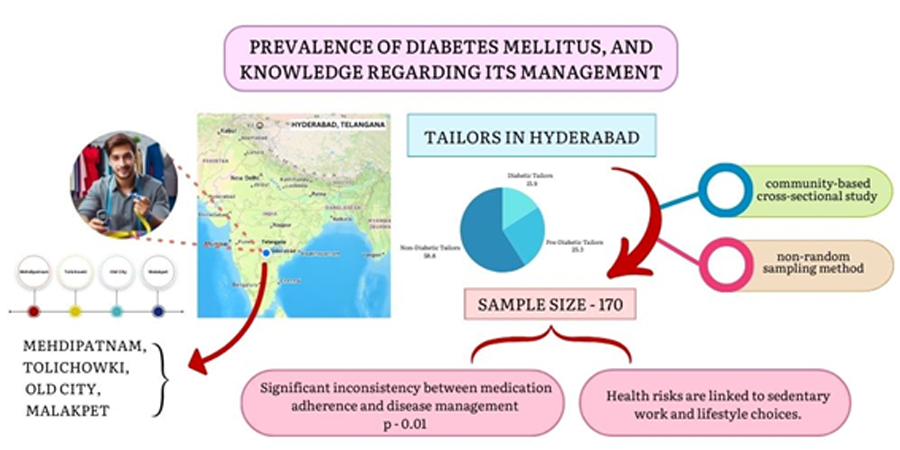
The rising diabetes prevalence in developing countries highlights a critical public health challenge linked to lifestyle changes and limited awareness of disease management. This study addresses the gap in understanding diabetes prevalence and management knowledge among sedentary occupational groups, such as tailors. This study aims to assess the prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus (DM) and evaluate knowledge regarding its management among tailors in Hyderabad. This community-based cross-sectional study assessed the prevalence of DM and evaluated knowledge about its management among tailors in Hyderabad, a group particularly at risk due to their sedentary work environments and limited awareness of diabetes management. Data were collected from 170 tailors aged 30–60 years across four localities in Hyderabad using a structured questionnaire and random blood glucose level checks. Results indicated that 58.8% of participants had normal glucose levels, 25.3% were pre-diabetic, and 15.9% were diabetic. Diabetes (19.4%) and hypertension (22.9%) were common, though only 37.1% adhered to regular medication. Irregular dietary habits were noted, with 61.8% skipping meals occasionally and 45% consuming outside food monthly. The mean blood glucose level was 146.85 mg/dL (SE: 3.92 mg/dL), with 97.1% consuming tea or coffee daily and 48.2% eating street food monthly. This study highlighted that Tailors, who tend to have sedentary work environments, are at particular risk due to a lack of awareness about diabetes, its management, proper nutrition normal Blood glucose, values and complications of DM.
Downloads
References
Assah, F., & Mbanya, J. C. (2017). Diabetes in sub-saharan Africa. Diabetes mellitus in developing countries and underserved communities, 33-48. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-41559-8_3
Carlsson, S., Andersson, T., Talbäck, M., & Feychting, M. (2020). Incidence and prevalence of type 2 diabetes by occupation: results from all Swedish employees. Diabetologia, 63, 95-103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-019-04997-5
Chandrupatla, S., Khalid, I., Muthuluri, T., Satyanarayana, D., & Tavares, M. (2020). Diabetes and prediabetes prevalence among young and middle aged adults, and geographic differences in india- national family health survey. Epidemiology and Health, e2020065. https://doi.org/10.4178/epih.e2020065
Dagogo-Jack, S. (2017). Primary prevention of type 2 diabetes: an imperative for developing countries. Diabetes mellitus in developing countries and underserved communities, 7-31. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-41559-8_2
Das, A., Mithal, A., Kumar, K., Unnikrishnan, A., Kalra, S., Thacker, H., & Joshi, S. (2019). Rationale, study design and methodology of the landmarc trial: a 3‐year, pan‐india, prospective, longitudinal study to assess management and real‐world outcomes of diabetes mellitus. Diabetic Medicine, 37(5), 885-892. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.14171
Dewi, F., & Hinchliffe, R. J. (2020). Foot complications in patients with diabetes. Surgery (Oxford), 38(2), 108-113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mpsur.2019.12.002
Diolindo, P. C., Dourado, L. M. S., Pinto, I. D. C. R., Barbosa, K. P. S., da Silva Xavier, A. C. M., Moura, S. M. S., & Bastos, K. D. A. S. (2023). Cases of amputation in patients with type 2 diabetes in the state of Piauí during the years 2002 to 2013. GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 24(1), 350-355. https://doi.org/10.30574/gscbps.2023.24.1.0289
Grimani, A., Aboagye, E., & Kwak, L. (2019). The effectiveness of workplace nutrition and physical activity interventions in improving productivity, work performance and workability: a systematic review. BMC public health, 19, 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-8033-1
International Diabetes Federation, 2019. IDF Diabetes Atlas. http://diabetesatlas.org/upload/resources/material/20200302_133351_IDFATLAS9e-final-web.pdf
Kuruvilla, A., Mishra, S., & Ghosh, K. (2023). Prevalence and risk factors associated with non-communicable diseases among employees in a university setting: A cross-sectional study. Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, 21, 101282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cegh.2023.101282
Lagad, A. (2023). Clinical study of add on effect of triphaladaruadi kwatha (vangsenokta) along with antidiabetic drug in management of prameha (non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus- niddm). International Journal of Ayurvedic Medicine, 14(3), 843-850. https://doi.org/10.47552/ijam.v14i3.3744
Li, A. K., & Nowrouzi-Kia, B. (2017). Impact of diabetes mellitus on occupational health outcomes in Canada. The international journal of occupational and environmental medicine, 8(2), 96. https://doi.org/10.15171/ijoem.2017.992
Malik, V. S., & Hu, F. B. (2022). The role of sugar-sweetened beverages in the global epidemics of obesity and chronic diseases. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 18(4), 205-218. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-021-00627-6
Mathur, P., Leburu, S., & Kulothungan, V. (2022). Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of diabetes in india from the countrywide national ncd monitoring survey. Frontiers in Public Health, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.748157
Mohanty, A. (2024). Prevalence of hypogonadism in male type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a cross-sectional study. International Journal of Medical and Biomedical Studies, 8(3). https://doi.org/10.32553/ijmbs.v8i3.2795
Nakazawa, S., Fukai, K., Furuya, Y., Kojimahara, N., Hoshi, K., Toyota, A., & Tatemichi, M. (2022). Occupations associated with diabetes complications: a nationwide-multicenter hospital-based case-control study. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 186, 109809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2022.109809
Park, J. H., Moon, J. H., Kim, H. J., Kong, M. H., & Oh, Y. H. (2020). Sedentary lifestyle: overview of updated evidence of potential health risks. Korean journal of family medicine, 41(6), 365. https://doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.20.0165
Patruni, M. & Narsaiah, C. (2020). Observational study on ocular manifestations in type 2 diabetes patients attending the ophthalmology department, at rvm hospital, south india. International Journal of Medical Ophthalmology, 2(2), 25-28. https://doi.org/10.33545/26638266.2020.v2.i2a.37
Pradeepa, R. & Mohan, V. (2021). Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes in india. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology, 69(11), 2932-2938. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijo.ijo_1627_21
Reyes, C. M., & Cornelis, M. C. (2018). Caffeine in the diet: country-level consumption and guidelines. Nutrients, 10(11), 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111772
Safieddine, B., Grasshoff, J., Geyer, S., Sperlich, S., Epping, J., & Beller, J. (2024). Type 2 diabetes in the employed population: do rates and trends differ among nine occupational sectors? An analysis using German health insurance claims data. BMC Public Health, 24(1), 1231. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18705-5
Sarkar, D., Dalal, R., & Sarkar, S. (2020). Study on prevalence of risk factors of diabetes among adult population in a rural area of west bengal, india. International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health, 7(2), 701. https://doi.org/10.18203/2394-6040.ijcmph20200452
Shekhar, R., Surit, R., Keshari, J., Prakash, P., & Kumari, S. (2023). Assessment of cardio-vascular disease risk in diabetic population of northern india. International Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Research, 10(2), 118-122. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijcbr.2023.019
Sindhuja, S. (2024). Diabetic technology in india: status, barriers, and future prospects. Wearable Technology, 4(1), 2645. https://doi.org/10.54517/wt.v4i1.2645
Sun, Y., You, W., Almeida, F., Estabrooks, P., & Davy, B. (2017). The effectiveness and cost of lifestyle interventions including nutrition education for diabetes prevention: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 117(3), 404-421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2016.11.016
Tamiya, H., Tamura, Y., Nagashima, Y., Tsurumi, T., Terashima, M., Ochiai, K., & Yasu, T. (2023). Long-Term Tailor-Made Exercise Intervention Reduces the Risk of Developing Cardiovascular Diseases and All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Diabetic Kidney Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(2), 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12020691
Tjahjono, C. T., & Arthamin, M. (2024). Sedentary lifestyle as a leading cause of some diseases and disability. Clinical and Research Journal in Internal Medicine, 5(1), 60-85. https://doi.org/10.21776/ub.crjim.2024.005.01.09
Unnikrishnan, A., Sahay, R., Phadke, U., Sharma, S., Shukla, R., Viswanathan, V., & Verberk, W. (2022). Cardiovascular risk in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients in india. Plos One, 17(3), e0263619. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263619
Vinothkumar, S., Priya, K. C., Vijayakumar, M., & Manivannan, T. (2021). Effectiveness of using staircase as a lifestyle modification among sedentary workers of a municipal corporation in improving fitness level- an interventional study. International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health, 8(4), 1733. https://doi.org/10.18203/2394-6040.ijcmph20211226
World Health Organization. (2024). Global diabetes report.
Yong, H. Y., Mohd Shariff, Z., Mohd Yusof, B. N., Rejali, Z., Bindels, J., Tee, Y. Y. S., & van Der Beek, E. M. (2020). High physical activity and high sedentary behavior increased the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus among women with excessive gestational weight gain: a prospective study. BMC pregnancy and childbirth, 20, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-020-03299-8
Copyright (c) 2024 Nasreen Begum, Saadia Fatima

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted to publish their work online in third parties as it can lead to wider dissemination of the work.






