Geographical Disparities in Blood Pressure and Dietary Patterns: A Comparative Study of Mountainous and Coastal Communities in Gorontalo, Indonesia
Abstract
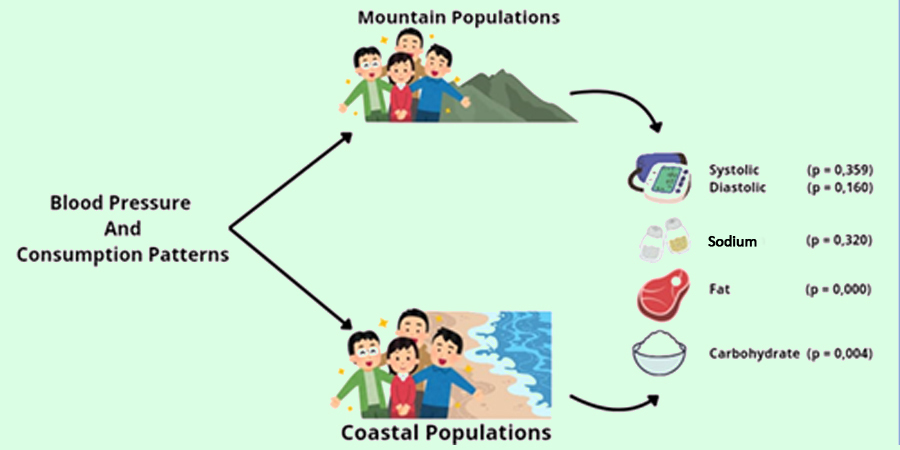
Hypertension, a leading cause of early death worldwide, affects 1.94% of the population in Gorontalo Regency, according to the local Health Department. However, limited studies have examined the relationship between hypertension prevalence and dietary patterns among mountain and coastal communities in this region. The purpose of this study was to explore differences in blood pressure and consumption patterns between people living in mountain areas and coastal areas in Gorontalo District. This research employed an analytic observational design with a cross-sectional approach. The study included 126 participants living in mountain and coastal areas of Gorontalo District, selected using a cluster random sampling technique. Data were collected using a 24-hour food recall questionnaire and a tension meter. The data were analyzed using the chi-square test. The findings revealed no significant differences in systolic blood pressure (p = 0.359, p > 0.05), diastolic blood pressure (p = 0.160, p > 0.05), or sodium consumption patterns (p = 0.324, p > 0.05) between residents of mountainous and coastal areas. However, significant differences were found in fat consumption patterns (p = 0.000, p < 0.05) and carbohydrate consumption patterns (p = 0.004, p < 0.05) between the two groups. It is recommended that residents regularly monitor their blood pressure to detect potential increases and reduce excessive salt consumption.
Downloads
References
Amelia, R. & Harahap, J. (2019). The role of nutritional status, age, genetic factors, and lifestyle on the hypertension prevalence among community in indonesian coastal area. International Journal on Advanced Science Engineering and Information Technology, 9(4), 1420-1426. https://doi.org/10.18517/ijaseit.9.4.5823
Amiri, P., Vahedi-Notash, G., Naseri, P., Khalili, D., Hashemi Nazari, S. S., Mehrabi, Y., & Hadaegh, F. (2019). National trends of pre-hypertension and hypertension among Iranian adolescents across urban and rural areas (2007–2011). Biology of sex differences, 10, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13293-019-0230-1
Andarwulan, N., Madanijah, S., Briawan, D., Anwar, K., Bararah, A., Saraswati, & Średnicka-Tober, D. (2021). Food Consumption Pattern and the Intake of Sugar, Salt, and Fat in the South Jakarta City—Indonesia. In Nutrients (Vol. 13, Issue 4). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041289.
Appiah, F., Ameyaw, E. K., Oduro, J. K., Baatiema, L., Sambah, F., Seidu, A. A., & Budu, E. (2021). Rural-urban variation in hypertension among women in Ghana: Insights from a national survey. BMC Public Health, 21, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-12204-7
Beddhu, S., Chertow, G. M., Cheung, A. K., Cushman, W. C., Rahman, M., Greene, T., Wei, G., Campbell, R. C., Conroy, M., Freedman, B. I., Haley, W., Horwitz, E., Kitzman, D., Lash, J., Papademetriou, V., Pisoni, R., Riessen, E., Rosendorff, C., Watnick, S. G., Whelton, P. K. (2018). Influence of baseline diastolic blood pressure on effects of intensive compared with standard blood pressure control. Circulation, 137(2), 134–143. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.030848.
Benjamin, E. J., Virani, S. S., Callaway, C. W., Chamberlain, A. M., Chang, A. R., Cheng, S., & Muntner, P. (2018). Heart disease and stroke statistics—2018 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation, 137(12), e67-e492. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000558
Byun, S. S., Mayat, Z. K., Aggarwal, B., Parekh, N., & Makarem, N. (2019). Quantity, Quality, and Timing of Carbohydrate Intake and Blood Pressure. Current Nutrition Reports, 8(3), 270–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13668-019-00277-1.
Chen, M. M., Zhang, X., Liu, Y. M., Chen, Z., Li, H., Lei, F., Qin, J. J., Ji, Y., Zhang, P., Cai, J., She, Z. G., Zhang, X. J., Lu, Z., Liu, H., & Li, H. (2021). Heavy Disease Burden of High Systolic Blood Pressure During 1990-2019: Highlighting Regional, Sex, and Age Specific Strategies in Blood Pressure Control. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, 8(December). https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2021.754778.
Farapti, F., Fatimah, A., Astutik, E., Hidajah, A., & Rochmah, T. (2020). Aware ness of salt intake among community-dwelling elderly at coastal area: the role of public health access program. Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, 2020, 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8793869
Flint, A. C., Conell, C., Ren, X., Banki, N. M., Chan, S. L., Rao, V. A., Melles, R. B., & Bhatt, D. L. (2019). Effect of Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure on Cardiovascular Outcomes. New England Journal of Medicine, 381(3), 243–251. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1803180 .
Food and Agriculture Organization. (2017). Dietary assessment. FAO Knowledge Repository
Gorontalo District Health Office. (2018a). Data Kesehatan Penyakit Tidak Menular Hipertensi.
Gorontalo District Health Office. (2018b). Profil Kesehatan Provinsi Gorontalo.
Grillo, A., Salvi, L., Coruzzi, P., Salvi, P., & Parati, G. (2019). Sodium intake and hypertension. Nutrients, 11(9), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11091970.
Harris, H., Ooi, Y., Lee, J., & Matanjun, P. (2019). Non-communicable diseases among low income adults in rural coastal communities in eastern sabah, malaysia. BMC Public Health, 19(S4). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-6854-6
Harter, R. (2005). NORC’s 1990 Sampling Design (K. B. T.-E. of S. M. Kempf-Leonard (ed.); pp. 883–891). Elsevier. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/B0-12-369398-5/00323-6.
Irwanto, F. S., Hasni, D., Anggraini, D., & Yulhasfi Febrianto, B. (2023). Hubungan Pola Konsumsi Lemak Dan Sodium Terhadap Tekanan Darah Pada Pasien Hipertensi Perempuan Etnis Minangkabau. Scientific Journal, 2(2), 62–73. https://doi.org/10.56260/sciena.v2i2.82
Ismah, Z., Purnama, T., Falefi, R., Mawar, L., Lestari, C., & Nst, C. (2021). Estimation of hypertension risk from lifestyle factors in coastal populations. Jurnal Riset Kesehatan, 10(2), 84-89. https://doi.org/10.31983/jrk.v10i2.6726
Jacobsen, A. P., McKittrick, M., Daya, N., Al Rifai, M., & McEvoy, J. W. (2022). Isolated Diastolic Hypertension and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: Controversies in Hypertension - Con Side of the Argument. Hypertension, 79(8), 1571–1578. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.18458
Jiang, Y., Shen, Q., Tang, H., Liu, Y., Ju, Y., Liu, T., Cui, L., Li, J., & Wang, X. (2022). Association between Dietary Carbohydrate Intake and Control of Blood Pressure in Patients with Essential Hypertension. Healthcare (Basel, Switzerland), 10(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10112245.
Kandil, H., Soliman, A., Alghamdi, N. S., Jennings, J. R., & El-Baz, A. (2023). Using mean arterial pressure in hypertension diagnosis versus using either systolic or diastolic blood pressure measurements. Biomedicines, 11(3), 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030849
Khan, N. A., Rabkin, S. W., Zhao, Y., McAlister, F. A., Park, J. E., Guan, M., Chan, S., & Humphries, K. H. (2018). Effect of lowering diastolic pressure in patients with and without cardiovascular disease: Analysis of the SPRINT (Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial). Hypertension, 71(5), 840–847. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10177
Li, Q., Liu, C., Zhang, S., Li, R., Zhang, Y., He, P., Zhang, Z., Liu, M., Zhou, C., Ye, Z., Wu, Q., Li, H., & Qin, X. (2021). Dietary Carbohydrate Intake and New-Onset Hypertension: A Nationwide Cohort Study in China. Hypertension, 78(2), 422–430. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.16751
Li, Y., & Wang, Y. (2022). Effects of long-term exposure to high altitude hypoxia on cognitive function and its mechanism: a narrative review. Brain sciences, 12(6), 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060808
Lilin, L. (2024). Evaluation of complementary cupping therapy in the management of hypertension and triglyceride levels in coastal fishermen communities. Public Health of Indonesia, 10(2), 237-246. https://doi.org/10.36685/phi.v10i2.806
Meher, M., Pradhan, S., & Pradhan, S. R. (2023). Risk factors associated with hypertension in young adults: a systematic review. Cureus, 15(4). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.37467
Ministry of Health. (2019). Hari Hipertensi Dunia 2019 : “KnowYour Number, Kendalikan Tekanan Darah Dengan Cerdik”.
Mphekgwana, P. M., Malema, N., Monyeki, K. D., Mothiba, T. M., Makgahlela, M., Kgatla, N., & Sodi, T. (2020). Hypertension prevalence and determinants among Black South African adults in semi-urban and rural areas. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(20), 7463. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207463
Oktaviyani, P., Happy, M., Sari, N., Frisilia, M., & Satria, A. (2022). Prevalence and Risk Factors of Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus among the Indonesian Elderly. Makara Journal of Health Research, 26(1), 26–32. https://doi.org/10.7454/msk.v26i1.1329.
Prot-Bertoye, C., Lievre, L., & Houillier, P. (2022). The importance of kidney calcium handling in the homeostasis of extracellular fluid calcium. Pflügers Archiv-European Journal of Physiology, 474(8), 885-900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-022-02725-4
Basic Health Research. (2018). Hasil Utama Riskesdas 2018.
Siregar, A., Krisnasary, A., & Simbolon, D. (2021). Differences of fruit-vegetable consumption, blood pressure in highland and lowland. Jurnal Ilmu Dan Teknologi Kesehatan, 8(2), 158-173. https://doi.org/10.32668/jitek.v8i2.362
Verberk, W. J., & Mieke, S. (2016). Are blood pressure monitors affected by high altitude? In Heart Asia (Vol. 8, Issue 2, pp. 52–53). https://doi.org/10.1136/heartasia-2016-010814.
Wang, C., Almoosawi, S., & Palla, L. (2019). Day-Time Patterns of Carbohydrate Intake in Adults by Non-Parametric Multi-Level Latent Class Analysis-Results from the UK National Diet and Nutrition Survey (2008/09-2015/16). Nutrients, 11(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102476.
Wiliyanarti, P. (2024). Knowledge, eating patterns, and hypertension among elderly in the coastal areas of bangkalan, indonesia. International Journal of Public Health Science (Ijphs), 13(1), 276. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijphs.v13i1.23179
Yu, J., Thout, S. R., Li, Q., Tian, M., Marklund, M., Arnott, C., & Wu, J. H. (2021). Effects of a reduced-sodium added-potassium salt substitute on blood pressure in rural Indian hypertensive patients: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 114(1), 185-193. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqab054
Zhou, B., Perel, P., Mensah, G. A., & Ezzati, M. (2021). Global epidemiology, health burden and effective interventions for elevated blood pressure and hypertension. Nature Reviews Cardiology, 18(11), 785-802. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-021-00559-8
Copyright (c) 2024 Marselia Sandalayuk, Yeni Paramata, Ririn Pakaya, Maesarah Yasin, Herman Hatta, Nuryani Nuryani

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted to publish their work online in third parties as it can lead to wider dissemination of the work.






